Fig. 3.
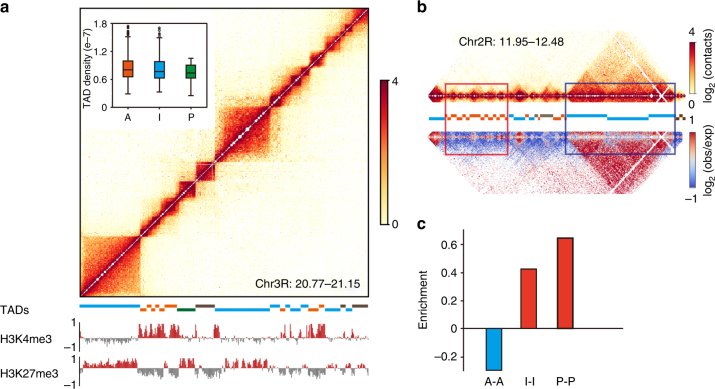
Epigenetic modifications only correlate with higher-order folding of the TADs but not the folding of individual TADs. a The TADs could be classified into four major types according to the enrichment of 15 histone modifications and non-histone chromosomal proteins within each TAD (Supplementary Methods). Shown is an example of the distribution of these types with active (orange bar below the heatmap), inactive (blue bar), polycomb (green bar), and undetermined (gray bar) chromatin within the TADs in a 380 kb region of chr3R. Inset: the extent of DNA condensation within the TADs, as determined from the average of contact frequencies between loci within the TAD. b Comparison of the frequency with which active or inactive TADs tend to interact with their immediately neighboring TADs. The upper heatmap shows the positions of the TADs, while the lower heatmap shows the significance of the observed contacts, with those colored red (blue) exhibiting much greater (lower) interaction strength than expected by chance (Methods) in a 530 kb region of chr2R. c The relative interaction strength (as shown in b) between pairs of TADs. A active, I inactive, P polycomb