Figure 3.
ATOH1+ IECs Give Rise to LGR5+ ISCs that Can Form Clonal Ribbons under Homeostatic Conditions
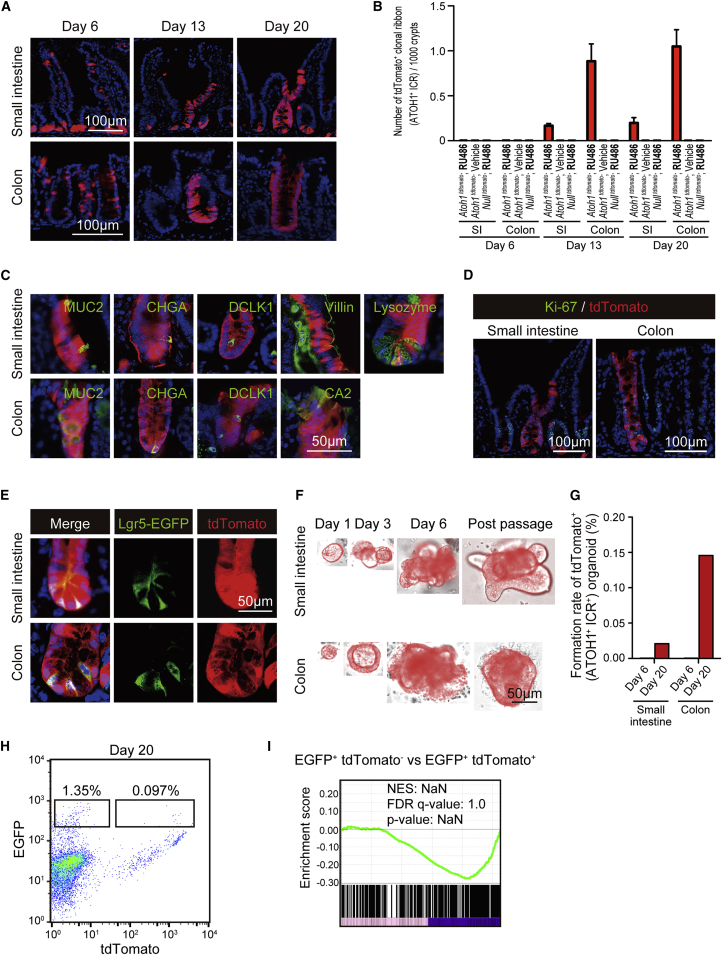
(A) Lineage tracing in Atoh1tdTomato mice showing the formation of tdTomato+ clonal ribbons (ATOH1+ICRs) in the small intestine and colon. Mice were treated by the five-dose protocol of RU486 and killed for analysis on day 6, day 13, and day 20.
(B) Quantification of ATOH1+ICR formation frequency in the small intestine and colon, using the tissue sections of Atoh1tdTomato mice or mice carrying Rosa26-LSL-tdTomato allele alone (Nulltdtomato). Atoh1tdTomato mice treated with vehicle alone (vehicle, n = 3), or Nulltdtomato mice treated with RU486 (n = 3) served as negative control. Atoh1+ICR was defined as those clusters of tdTomato+ cells completely occupying the whole crypt-villus unit, as assessed by the examination of at least three serial sections. The number of ATOH1+ICR was normalized against the total number of crypts. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM.
(C) Co-staining of cell-lineage markers, such as MUC2, CHGA, DCLK1, Villin, CA2, and Lysozyme (green) with tdTomato (red) on day 20.
(D) Co-staining of Ki-67 (green) and tdTomato (red) in the Atoh1+ICR observed on day 20.
(E) Fluorescence images of tdTomato+ cells (red) co-expressing Lgr5-EGFP (green) in the ATOH1+ICR of Lgr5EGFPAtoh1tdTomato mice on day 20. Mice were treated as described in (A).
(F) Successful establishment of tdTomato+ organoids from the small-intestinal and colonic tissues recovered from Atoh1tdTomato mice on day 20.
(G) The efficiency of tdTomato+ organoid formation was quantified using tissues collected from the Atoh1tdTomato mice. Total cumulative number of tdTomato+ organoids acquired from four mice is normalized by the total number of organoids.
(H) Representative flow plots showing the increased presence of Lgr5-EGFP+tdTomato+ IECs in the small intestine of the Lgr5EGFP-CreERT2Atoh1tdTomato mice on day 20 compared with the data on day 6 shown in Figure 2B.
(I) Designated cell fractions in (H) were subjected to microarray analysis and then compared and analyzed for the adult stem cell-specific gene set (M1999) by GSEA.
See also Figure S3.