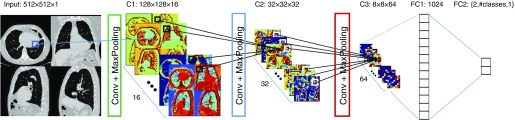
Figure 1.
The input of the convolutional neural network is a composite image of four canonical views of the computed tomography scan: an axial slice at the level of the mitral valve, a coronal slice taken at the level of the ascending aorta, and two sagittal slices at the level of the right and left hila. The image is analyzed with a convolutional neural network consisting of three convolutional layers (Conv) followed by max-pooling operations, each reducing the image size fourfold in each direction. At the end of the convolutional layers are two fully connected networks, the first one of 1,024 neurons and the second one of variable size depending on the problem at hand: classification, multiclass classification, or regression.