Figure 6.
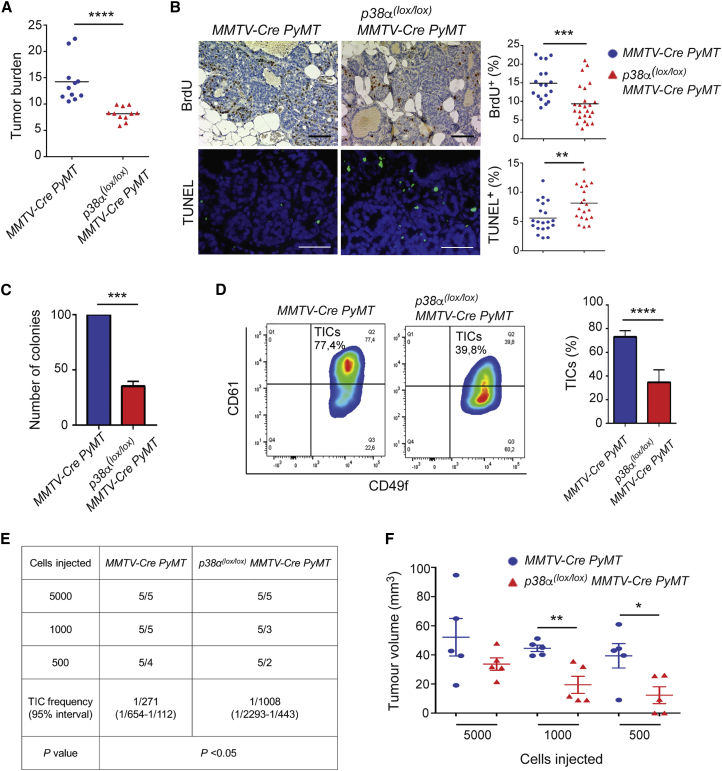
Depletion of p38α in Luminal Cells Impairs Mammary Tumor Growth and Reduces the Number of Tumor-Initiating Cells
(A) Tumor burden in mice of the indicated genotypes was determined at 14 weeks of age (n = 11 animals). ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.00005.
(B) Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) and TUNEL staining in mammary pre-neoplastic lesions from mice of the indicated genotypes (n = 20 animals). Quantifications are shown in the histograms. Scale bars, 10 μm. ∗∗p ≤ 0.005; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0005.
(C) Colonies formed in Matrigel by EpCAMhighCD49fmed luminal cells isolated from mammary pre-neoplastic lesions of mice with the indicated genotypes were quantified and values are expressed as percentage to the numbers in MMTV-Cre;PyMT mice (n = 3 independent experiments). ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0005.
(D) FACS plots for luminal cells isolated on the basis of CD61 and CD49f expression from mammary pre-neoplastic lesions. Quantifications shown in the histogram indicate the percentage of CD61+CD49f+ tumor-initiating cells (TICs) in mice of the indicated genotypes (n = 7 animals). ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.00005.
(E and F) Luminal cells were isolated from mammary pre-neoplastic lesions of mice with the indicated genotypes. The indicated numbers of cells were orthotopically injected into nude mice (n = 5 animals). Tumor incidence (E) and tumor volume (F) at 7 weeks after injection are shown. ∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗p ≤ 0.005.
See also Figure S4.