Fig 9. Decreasing cFLIP levels using shRNA results in decreased protection by TAPF.
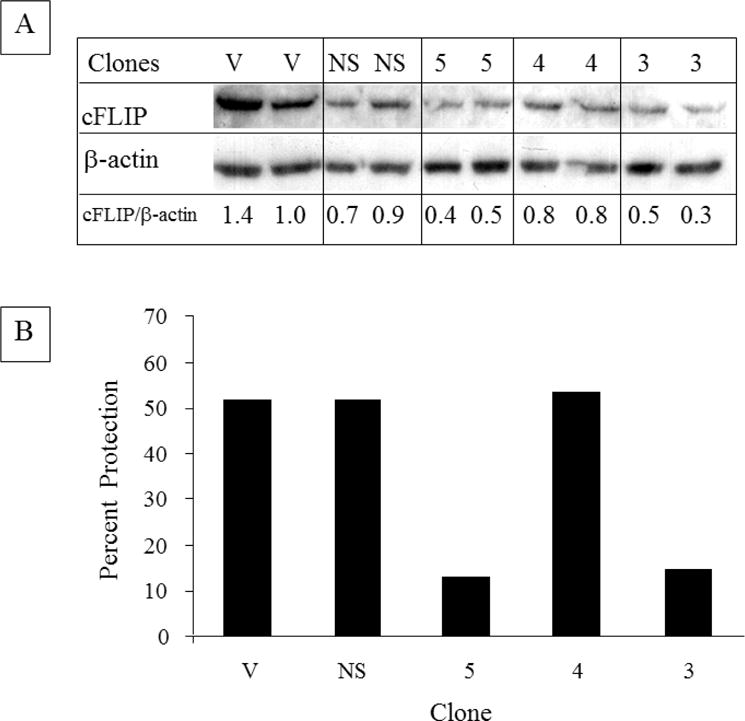
A: NHDF were infected with multiple cDNAs which encode either vector (V), an shRNA against GFP (NS), or three different shRNAs against cFLIP [5, 4, 3]. Following antibiotic selection, pools of clones from each were washed, lysed and equivalent amounts (10 μg) were analyzed by immunoblotting for cFLIP. The levels of cFLIP normalized to β-actin are indicated. Decreased cFLIP was observed in seven independent preparations of the pool of clone 3 and in five independent preparations of the pool of clone 5. B: pools of the clones described in A were treated with TAPF for 18h, TNF+CHX were added and viable cells were stained 24h later. Bar height represents the mean of each data set. For incubations with TAPF, n=2. For controls (i.e. CHX, TNF+CHX), n=4. Percent protection was calculated as described for Fig. 1A and utilized individual controls for each pool of clones. One representative experiment out of four is shown.
