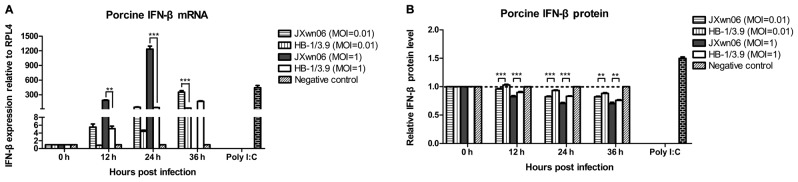
Figure 1.
Inhibition of the IFN-β protein expression in PRRSV-infected PAMs by post-transcriptional control. (A) The mRNA levels of porcine IFN-β in PRRSV-infected PAMs and (B) its protein expression levels in the culture supernatants of PRRSV-infected PAMs were detected by real-time PCR and ELISA, respectively. Primary PAMs were infected with JXwn06 or HB-1/3.9 at MOI of 0.01 or 1, and then the cell and supernatant samples harvested at 0, 12, 24 and 36 hpi, were measured by real-time PCR and ELISA, respectively, while mock-infected primary PAMs served as negative control and primary PAMs stimulated by 50 µg/ml poly I:C for 24 h were used as positive control. Relative expression level of IFN-β gene was analyzed using the ∆∆Ct method and the housekeeping gene RPL4 mRNA was used as an internal control. The IFN-β protein data are shown as relative expression levels normalized to negative control group at each time point, respectively. The data represent means ± standard error of the mean of three independent experiments (**P<0.01; ***P<0.001). Since the primary PAMs infected with JXwn06 at MOI of 1 were disrupted at 36 hpi, the data in relation to IFN-β mRNA transcription could not be analyzed. IFN-β, interferon-β.