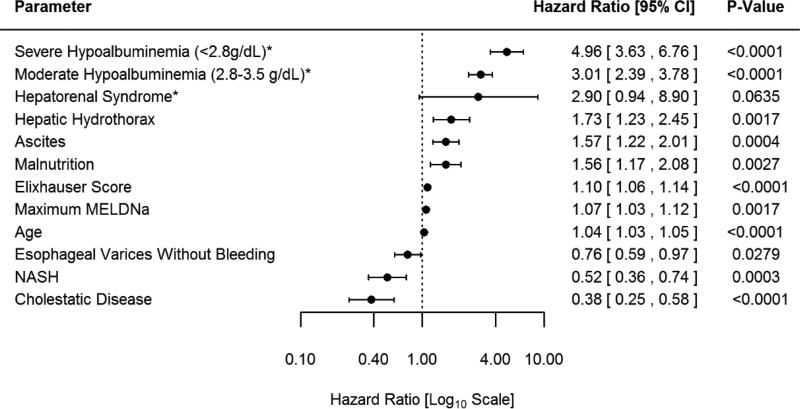
Figure 2. Multivariate Subdistribution Hazards Model.
*Reference >3.5g/dL
The Figure demonstrates the Hazard Ratio for risk factors for mortality determined by the multivariate subdistribution hazards model among patients with MELDNa ≤ 15 (Low-MELDNa). The model is adjusted for age, gender, race, insurance, Elixhauser score and maximum MELDNa score. Severe hypoalbuminemia is defined as maximum serum albumin <2.8g/dl during the study period. Moderate hypoalbuminemia is defined as a maximum serum albumin 2.8–3.5g/dl during the study period. In this model hepatorenal syndrome is not statistically significant, however in a subsequent model (figure 3) where interaction terms for transplant waitlist are introduced the main effect of hepatorenal syndrome is observed to be statistically significant p=0.0414 (HR 3.27 95% CI 1.048–10.23)
Abbrev: CI: confidence interval, g/dl: gram per deciliter, NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis MELDNa: Model for end-stage liver disease sodium