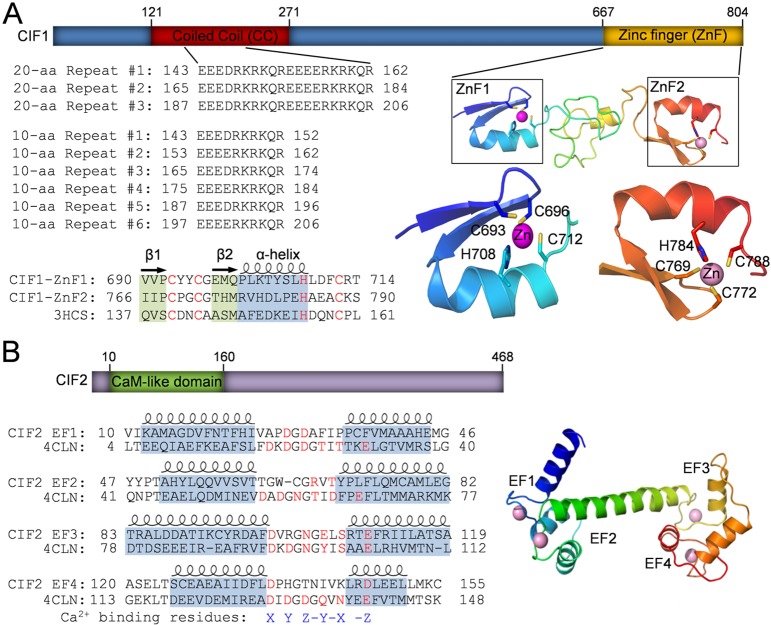
Fig. 1.
Identification of structural motifs in CIF1 and CIF2 by homology modeling. (A) Illustration of the conserved domains in CIF1. The coiled-coil (CC) motif located at the N-terminal portion of CIF1 contains a repetitive sequence composed of either three 20 aa repeats or six 10 aa repeats. The two CCHC-type zinc-finger (ZnF) motifs, ZnF1 and ZnF2, share similar folds and are predicted to be able to coordinate a zinc ion by the conserved CCHC residues (highlighted in red). Zinc-finger motifs were modeled using the crystal structure of TRAF6 (PDB code: 3HCS) as the template. (B) Illustration of the conserved domain in CIF2. The predicted calmodulin-like domain at the N-terminal portion of CIF2 possesses four EF-hand motifs, which is modeled using the crystal structure of Drosophila calmodulin as the template (PDB code: 4CLN). Note that all four EF-hand motifs lack one or more conserved residues (highlighted in red) required for coordinating the calcium ion.