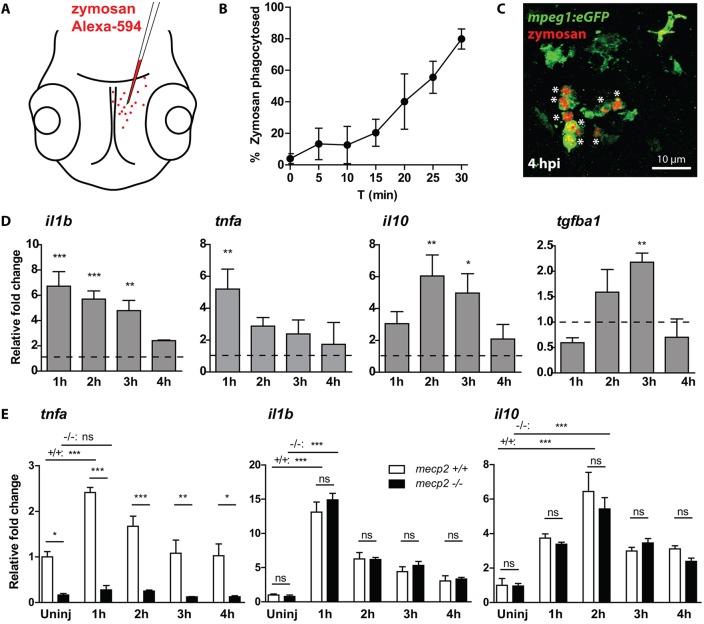
Fig. 4.
mecp2-null larvae are unable to increase tnfa expression during an acute inflammatory response. (A) Schematic of the injection of Alexa Fluor 594-labeled zymosan into the brains of 3 dpf zebrafish larvae. (B) The percentage of zymosan particles phagocytosed by Tg(mpeg1:eGFP)-positive cells in wild-type larvae was determined using confocal microscopy of samples fixed every 5 min after injection (n=5 larvae per time point). (C) Representative confocal micrograph of a wild-type Tg(mpeg1:eGFP) larva at 4 hpi. Asterisks indicate zymosan particles phagocytosed by Tg(mpeg1:eGFP)-positive cells. (D) qPCR was performed to determine the whole-organism gene expression level of il1b, tnfa, il10 and tgfb1 relative to the expression of the housekeeping gene tbp. Samples (n=3 with 10 embryos per sample) were taken at 1, 2, 3 and 4 hpi of zymosan or PBS as a control. The relative fold change of zymosan- versus PBS-injected samples is shown for each time point to account for a possible wounding effect by the injection itself. (E) qPCR was performed to determine the whole-organism expression level of il1b, tnfa, il10 and tgfb1 relative to the expression of the housekeeping gene tbp. Wild-type or mecp2-null samples (n=3 with 10 embryos per sample) were taken at 1, 2, 3 and 4 hpi of zymosan. The relative fold change of zymosan-injected larvae versus uninjected wild-type controls is shown for each time point to not exclude a potential different response in mecp2-null samples towards the wound caused by the injection. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test was used for all statistical analyses (***P<0.001; **P<0.01; *P<0.05; ns, not significant; data are representative of at least two individual experiments).