Fig. 5.
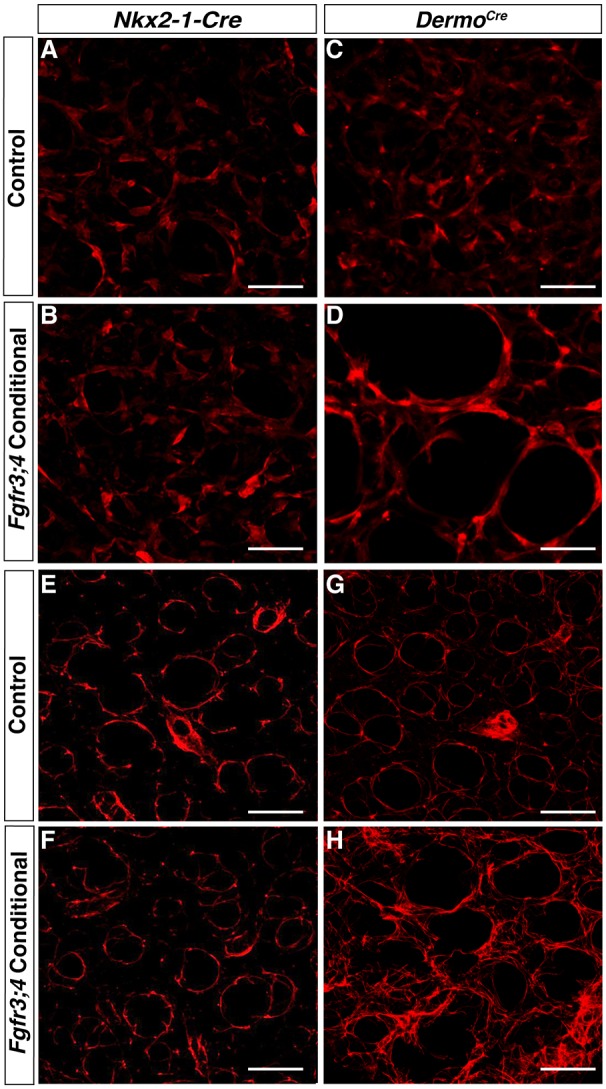
Loss of Fgfr3 and Fgfr4 activity in the mesenchyme leads to stretched myofibroblasts and disorganized elastin ECM. (A-D) Reconstructed 50 μm z-stacks of immunofluorescent staining for TAGLN (red) in the alveolar region of P8 Cre control (A,C) and Nkx2-1cre;Fgfr3;4 (B) or Dermo1cre;Fgfr3;4 (D) conditional mutant lungs. TAGLN-positive myofibroblasts were unaltered in the Nkx2-1cre;Fgfr3;4 conditional lung compared with control (A,B), but were enlarged in the Dermo1cre;Fgfr3;4 conditional lung compared with control (C,D). The latter phenotype is reminiscent of that seen in the Fgfr3;4 global mutant. (E-H) Reconstructed 50 μm z-stacks of immunofluorescent staining for elastin in the alveolar region of P8 Cre control (E,G) and Nkx2-1cre;Fgfr3;4 (F) or Dermo1cre;Fgfr3;4 (H) conditional mutant lungs. In the Nkx2-1cre;Fgfr3;4 conditional lung, the elastin fibers are primarily found around the alveolar entrance ring, similar to the control (E,F). In the Dermo1cre;Fgfr3;4 conditional lung, elastin is disorganized with multiple fibers running through the alveolar walls (G,H). This phenotype is reminiscent of that seen in the Fgfr3;4 global mutant. Scale bars: 100 μm.
