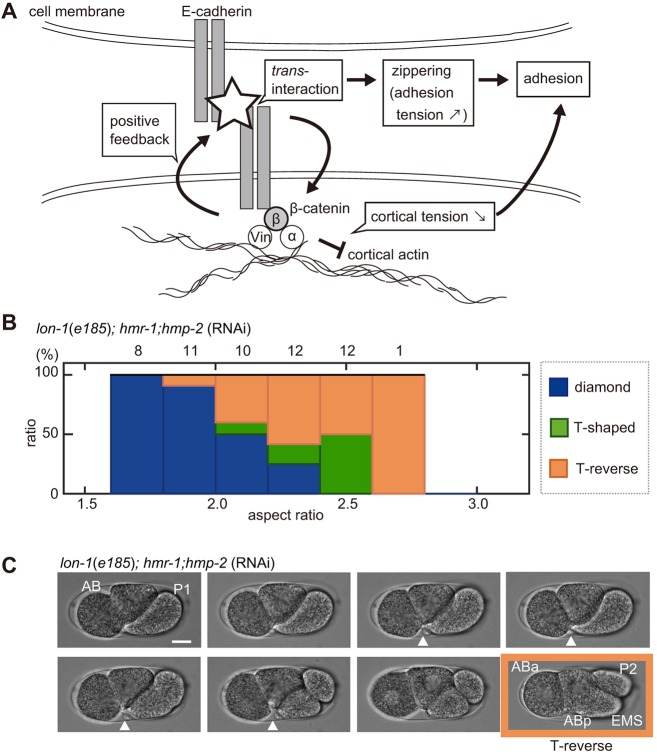
Fig. 7.
Impaired robustness of the diamond-type arrangement against eggshell deformation in the C. elegans embryo. (A) Schematic representation of E-cadherin- and β-catenin-mediated cell adhesion at cell boundaries. α-catenin (α) and Vinculin (Vin) mediate interactions with the cortical actin. (B) Relationship between the percentage of the patterns of cell arrangements found (blue, diamond type; green, T-shaped type; orange, T-reverse type) and the ARs in the hmr-1; hmp-2-knockdown strain on a lon-1(e185) background; the numbers above the bars represent the number of embryos. (C) Sequential snapshots acquired when breakage of cell adhesion between ABa and EMS cells occurred in the hmr-1; hmp-2-double-knockdown strain with lon-1(e185) mutant background. White arrowheads indicate cell–cell contact between ABa and future EMS cell. The T-reverse-type cell arrangement (absence of cell–cell contact between ABa and P2 cells, and ABa and EMS cells) was formed at the four-cell stage (orange). Scale bar: 10 μm.