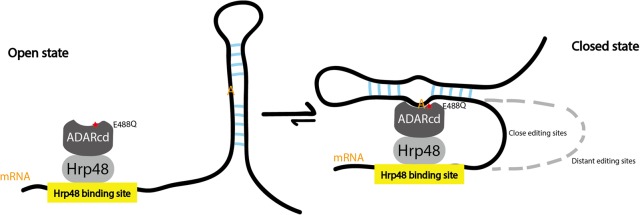
FIGURE 6.
Proposed model: Hyper-TRIBE is better able to shift the equilibrium toward the closed state. When HyperTRIBE binds to a target mRNA, adenosines in potential double-stranded regions are candidate substrates for binding to the HyperADARcd moiety. More proximal adenosines will be accessible for HyperADARcd binding with a small RNA loop, whereas more distant adenosines require a larger and more destabilizing RNA loop. We suggest that the Hyper-ADARcd, with its E488Q mutation, is better able to shift the equilibrium toward the closed state, perhaps by binding more tightly to the flipped adenosine. However, the exact mechanism by which the E488Q mutation increases the editing/deamination rate is unknown (Kuttan and Bass 2012).