Figure 2.
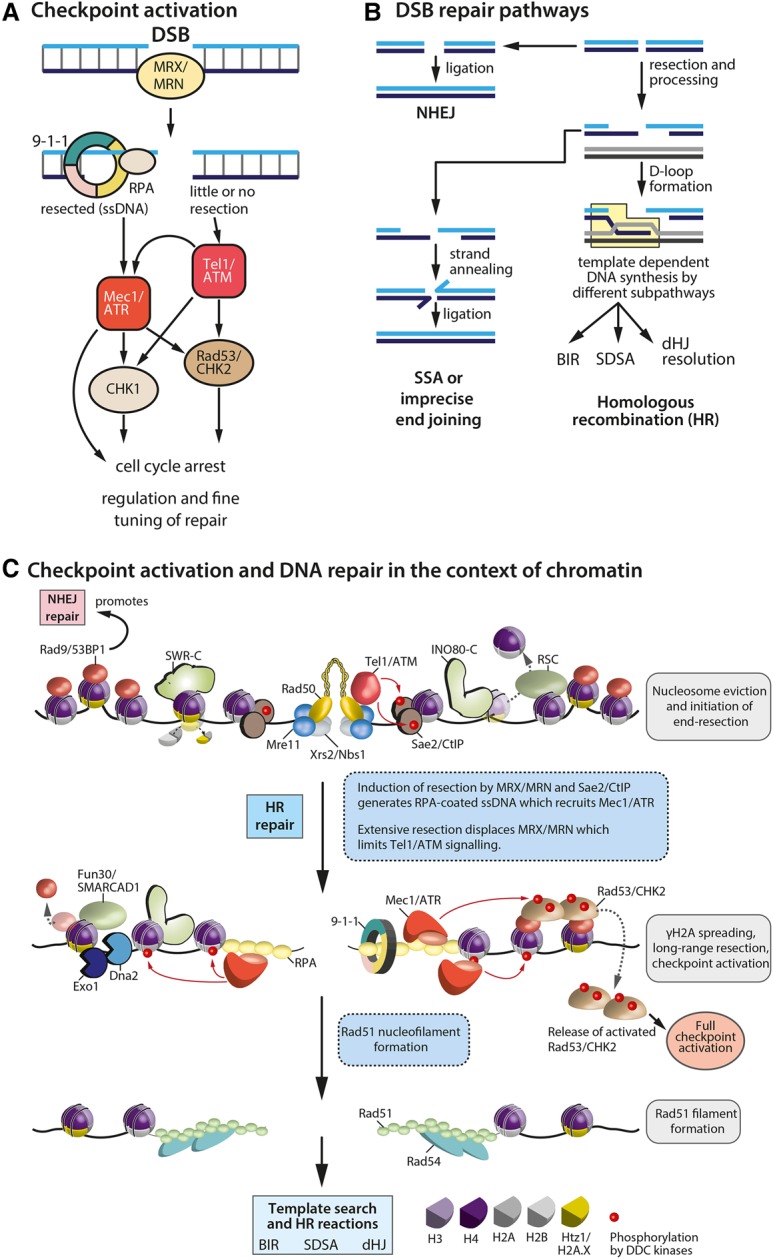
Checkpoint activation and DSB repair in the context of chromatin. (A) Proteins involved in DDC activation in response to a DSB. The checkpoint stalls the cell cycle and coordinates repair proteins acting at the site of damage. Mammalian proteins are capitalized. (B) Three of the main DSB repair pathways are shown: NHEJ, single-strand annealing (SSA), and HR (see the text for details). HR intermediates are resolved by subsequent pathways, resulting in different repair outcomes (light-blue box). (BIR) Break-induced replication; (SDSA) synthesis-dependent strand annealing; (dHJ) double-Holliday junction. (C) Effects of both the DDC and the DSB repair functions integrate on the chromatin template. The key steps and the main players during homology-directed DSB repair are listed. The first panel highlights early steps after DSB formation. The second panel illustrates DSB processing and spreading of the DDC signal. The last panel shows the Rad51 nucleofilament before homology search and after strand invasion and repair.
