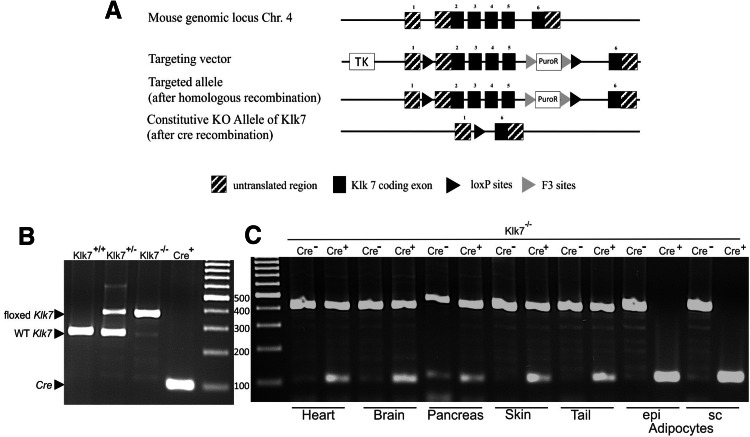
Fig. 1.
Targeting strategy for the generation of ATKlk7 −/− mice. a Schematic representation of the loxP-flanked Klk7 allele before and after crossing with transgenic animals expressing Cre-recombinase under the Fabp4 promoter. The targeting vector consisted of 2 kb of the murine Klk7 gene, comprising exon 2–5 flanked by loxP sites and two selection markers herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase (TK) and puromycin N-acetyltransferase (PuroP). F3 sites flanked the PuroP selection marker. The knockout (KO) allele, shown under the floxed allele, is characterized by the deletion of exons 2–5. The constitutive KO occurs by Cre-mediated deletion of exon 2–5 and the selection marker. b Genomic DNA from WT (Klk7+/+, predicted PCR product size of 276 bp), heterozygous floxed (Klk7+/−, predicted PCR products of 276 and 402 bp) or homozygous floxed Klk7 mice (Klk7−/−, predicted PCR product of 402 bp) was used as template for PCR of the floxed Klk7 allele and from Fabp4-Cre+ mice (Cre+, predicted PCR product of 100 bp) as template for PCR of the Cre allele. c Fabp4-Cre+_Klk7−/− (ATKlk7−/−) mice exhibit an adipocyte/AT specific loss of the floxed Klk7 allele. Genomic DNA from selected tissues (heart, brain, pancreas, skin, tail) and of isolated adipocytes from epigonadal (epi) and subcutaneous (sc) AT of Klk7−/− mice with and without the Fabp4_Cre transgene was used as template for PCR of the Klk7−/− and the Cre allele. Arrows indicate PCR products