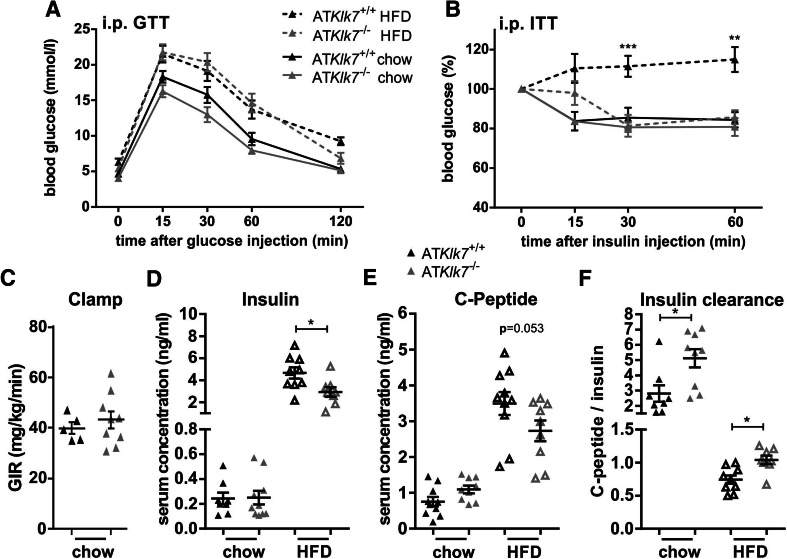
Fig. 4.
Parameters of glucose metabolism, insulin sensitivity and adipokine secretion in ATKlk7 −/− mice. a Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance (GTT) and b insulin tolerance (ITT) after chow (24 weeks of age) and HFD (14 weeks of age). Glucose tolerance was not different between ATKlk7 −/− and control mice, both under chow and HFD conditions. Under HFD, Klk7 deficiency in AT resulted in significantly improved insulin sensitivity (n = 10–13). c Hyperinsulinemic–euglycemic clamp shows a slight increase in glucose infusion rate for ATKlk7 −/− compared to control mice under chow diet (n = 5–9). Mice were fasted overnight and insulin (d) and C-peptide (e) levels were measured in serum and the ratio was calculated as a surrogate parameter of insulin clearance (f) in ATKlk7 −/− and control mice under chow (32 weeks of age) and HFD (20 weeks of age) conditions (n = 8–10). Data are presented as mean ± SEM and for each diet condition differences between genotypes were tested for statistical significance by a two-tailed Student’s t test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001