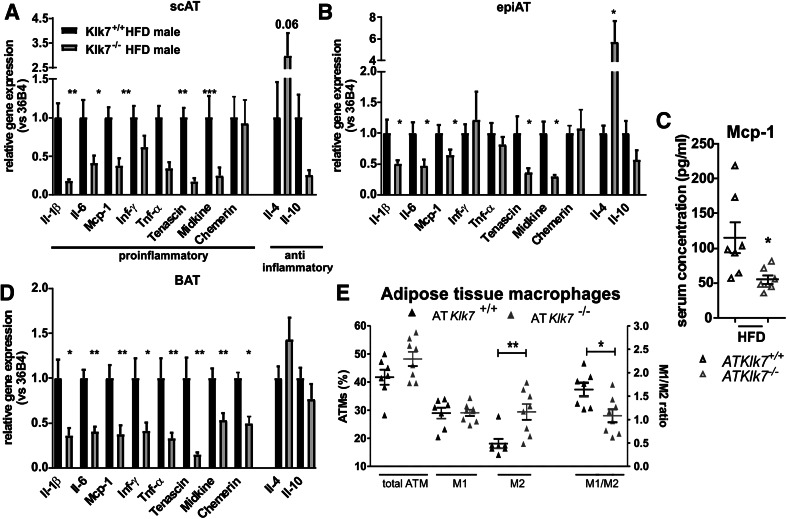
Fig. 8.
ATKlk7 −/− mice exhibit lower expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in adipose tissue and a shift in adipose tissue macrophages (ATM) toward an M2 phenotype in response HFD. a, b, d Expression of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in subcutaneous (a) and epigonadal (b) AT and BAT (d) (n = 6–8). Expressions of Il-1β, Il-6, Mcp-1, Tenascin and Midkine were significantly lower in both fat depots of ATKlk7 −/− compared to control mice. Tnf-α and Inf-γ were lower in sc AT of ATKlk7 −/− mice, but unchanged in epigonadal AT. Anti-inflammatory Il-4 was increased in epi AT and in tendency in sc AT of ATKlk7 −/− mice. AT Il-10 expression was not significantly different between the genotypes. c Circulating levels of Mcp-1 were significantly lower after HFD in ATKlk7 −/− mice, indicating amelioration of not only local but also systemic inflammation in the ATKlk7 −/− mice (n = 7 per genotype). e Analysis of macrophage polarization in epigonadal AT. While total ATM percentage and M1-polarized macrophages were unaffected by HFD in ATKlk7 −/− mice, the number of anti-inflammatory M2-polarized macrophages was significantly higher compared to control mice. This is also reflected by the significantly altered M1/M2 ratio ATKlk7 −/− compared to control mice (n = 7–8 per genotype). Data are presented as mean ± SEM and for each gene expression differences between genotypes were tested for statistical significance by a two-tailed Student’s t test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001