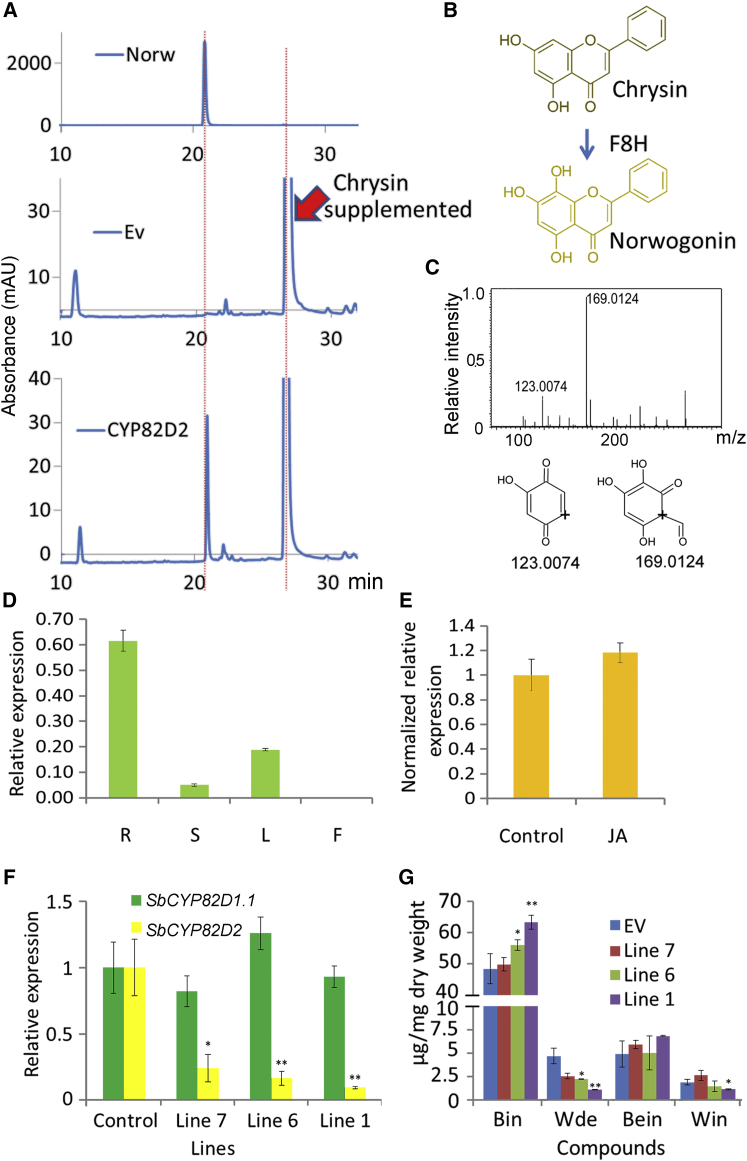
Figure 5.
Characterization of SbCYP82D2 Enzyme Activity, Gene Expression Analysis, and RNAi of SbCYP82D2 in Hairy Roots.
(A) HPLC analysis of yeast samples incubated with chrysin in vivo. Top, norwogonin standard; middle, yeast carrying empty vector; bottom, yeast expressing SbCYP82D2, where a new peak with the same retention time as norwogonin was found. Norw, norwogonin.
(B) The proposed reaction catalyzed by SbCYP82D2.
(C) MS2 and fragmentation patterns of the new compound produced by SbCYP82D2 expressed in yeast. The fragmentation patterns were identical to those for norwogonin.
(D) Relative levels of SbCYP82D2 transcripts compared with β-actin determined by qRT–PCR analyses performed on cDNA from total RNA extracted from different organs. R, roots; S, stems; L, leaves; F, flowers.
(E) Relative expression of SbCYP82D2 following MeJA treatment for 24 h. The expression levels were normalized to corresponding values from mock treatments.
(F) Silencing of SbCYP82D2 in RNAi hairy roots was measured by monitoring relative transcript levels by qRT–PCR.
(G) Measurements of RSFs from the SbCYP82D2 RNAi lines used for transcript analysis. Bin, baicalin; Wde, wogonoside; Bein, baicalein; Win, wogonin.
SEs were calculated from three biological replicates. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (Student's t-test).