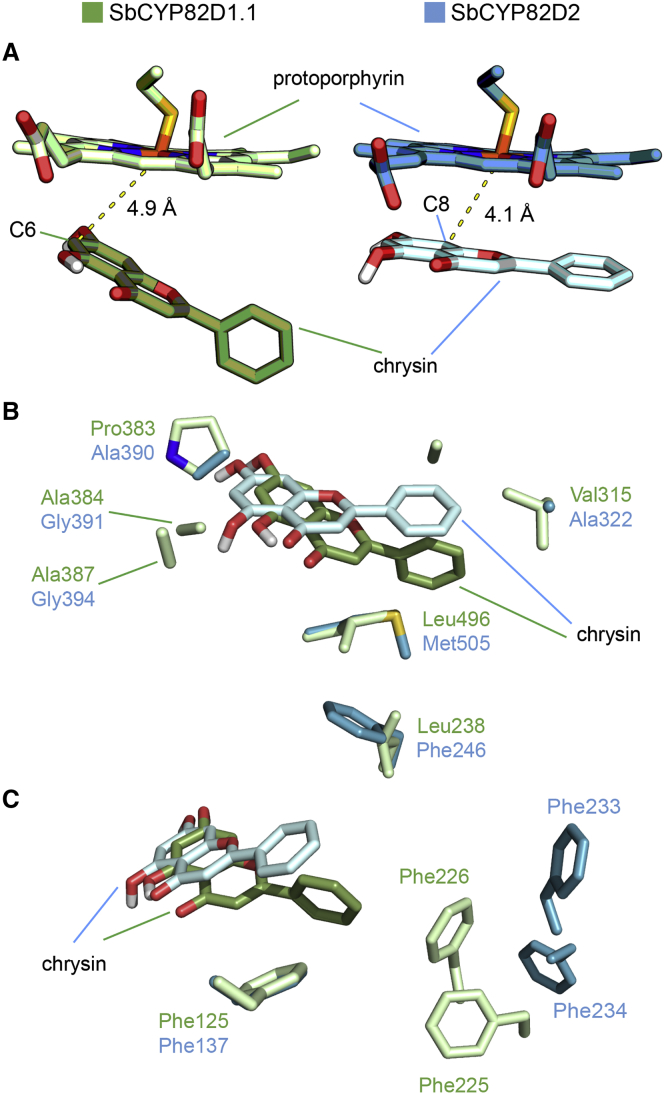
Figure 6.
Structural Modeling of Chrysin Binding with SbCYP82D1.1 and SbCYP82D2.
(A) Ligand modeling results indicate that chrysin binds in different orientations in the SbCYP82D1.1 (green) and SbCYP82D2 (blue) binding sites. The tilted conformation of chrysin in the SbCYP82D1.1 active site causes the 6-carbon (C6) to be 4.9 Å away from the protoporphyrin iron, whereas the flat conformation in the SbCYP82D2 active site places the 8-carbon (C8) 4.1 Å away from the protoporphyrin iron.
(B) Bulky substrate-proximal residues in SbCYP82D1.1 such as Pro383, Ala384, and Ala387 may shift chrysin binding, while additional bulky residues on the opposite end such as Val315, Leu496, and Leu238 may cause the substrate to tilt.
(C) Phe125, Phe225, and Phe226 in SbCYP82D1.1 form a nearby hydrophobic pocket that may stabilize the tilted binding of chrysin. The corresponding residues in SbCYP82D2 are located too far away to mediate the same effect.