Figure 3. Diagram of reported Pura nucleic acid-binding and protein-binding regions in relation to signature Pur domains and to structural features from crystallographic studies. A. Box diagram map of nucleic acid and protein binding regions.
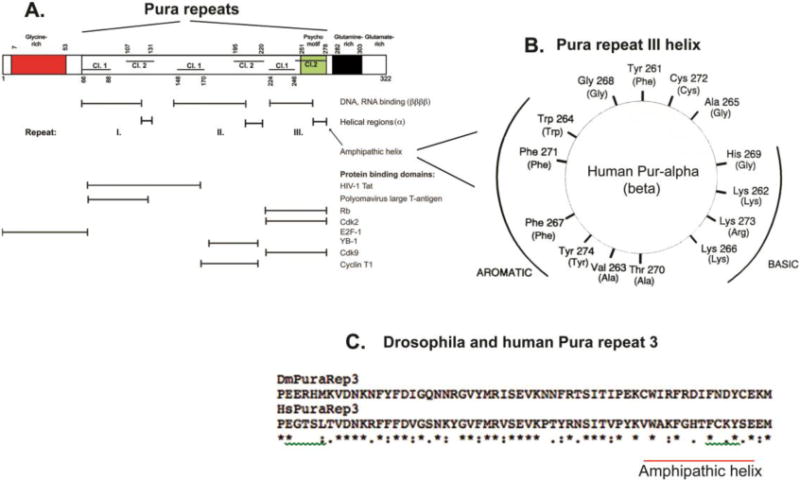
Red indicates the region containing long tracts of poly-Gly. Structure: not determined. Green indicates the psycho motif, which is present in Repeat III of eukaryotic organisms and in the only repeat of bacterial Pura (Figure 1). It is present in several other DNA replicative proteins (Ma et al., 1994). Structure: alpha helix (a). Black indicates a Gln-rich region in mammalian Pura proteins. Structure: not determined. Horizontal lines in the boxes denote the Class 1 (lower lines) and Class 2 (upper lines) portions of each Pur repeat. Note that sequences of variable length separate each repeat and the portions of Repeats I and II. X-ray crystallographic analyses of Drosophila Pura reveal that the N-terminal sequence of each repeat, comprising all of Class 1 and a part of Class 2, is structured as four beta-strands comprising a beta sheet, reported to be primarily involved in nucleic acid binding (Graebsch et al., 2009; Weber et al., 2016). The C-terminal 14–15 amino acids of each repeat are in an alpha helical structure (a) primarily involved in protein binding. Horizontal lines with vertical stops below the map denote indicated Pura regions. Positions of reported protein binding are from (White et al., 2009). B. Human Pura amphipathic helix. The wheel is a 2-dimensional depiction looking down the axis of the Repeat III 14 amino acid helix. Aromatic residues are present on one side of the helix and basic residues on the other. For comparison, the homologous region of Purb is included on the wheel. Purb has a very similar amphipathic helix, as shown by the residues in parentheses. C. Alignment comparison of human vs. Drosophila Repeat III. Alignment is with the Clustal Omega algorithm. The human Pura sequence is from Genbank M96684.1. Drosophila melanogaster is from Genbank AF021259.1. The entire gene coding sequence of human Pura is shown compared to that of Drosophila in Supplementary Fig. 1S. In Fig. 3C, stars indicate amino acid identities; one dot indicates a substitution; two dots indicate a conservative substitution. Beta sheet and helical structural regions are conserved. The helical regions in the psycho motifs differ. The human Rb binding site is altered in Drosophila. Drosophila lacks a double-sided amphipathic helix, but residues on the aromatic side of the helix are strongly conserved.(Figure 3B from Bergemann et al., 1992, Mol Cell Biol, 12, 5673–5682 used with permission.)
