FIGURE 3.
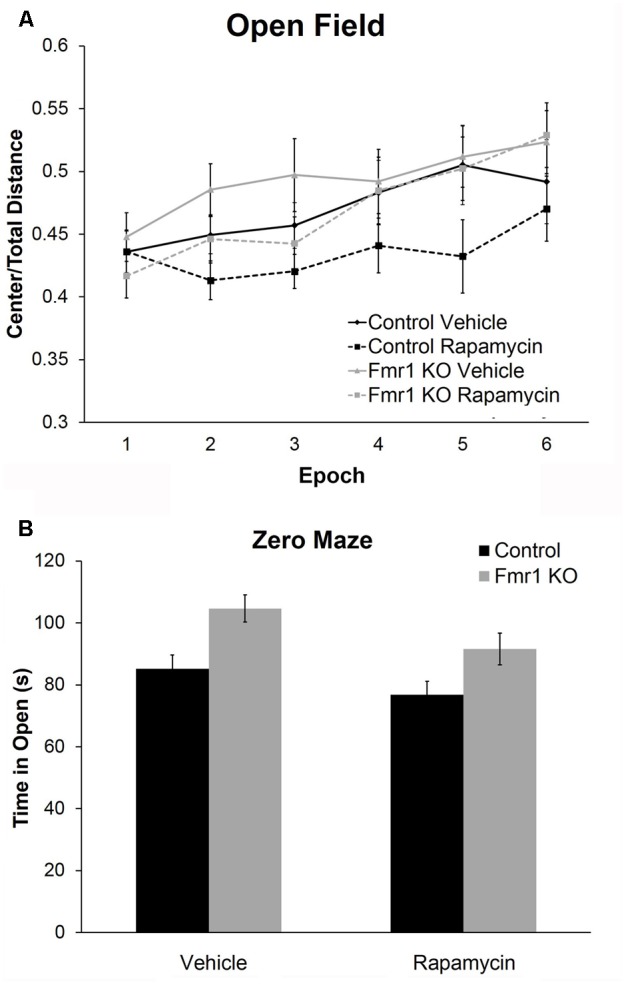
Rapamycin increased anxiety in control and Fmr1 KO mice. (A) Regarding the ratio of distance traveled in the center to total distance traveled in the open field, there was a near significant main effect of genotype (p = 0.083) suggesting that Fmr1 KO mice tended to show a decrease in anxiety. There was also a near significant main effect of treatment (p = 0.081) suggesting that, regardless of genotype, rapamycin may have increased anxiety. Points represent mean ± SEM in 26 vehicle-treated control, 23 rapamycin-treated control, 18 vehicle-treated Fmr1 KO, and 21 rapamycin-treated Fmr1 KO. (B) In the zero maze, there was a significant main effect of genotype (p = 0.001) showing that Fmr1 KO mice spent more time in the open arms compared to control mice. Again, this shows that Fmr1 KO mice have reduced anxiety. There was also a significant main effect of treatment (p = 0.026) showing that, regardless of genotype, rapamycin decreased the time spent in the open arms, indicating that rapamycin increases anxiety. Bars represent mean ± SEM in 27 vehicle-treated control, 28 rapamycin-treated control, 16 vehicle-treated Fmr1 KO, and 19 rapamycin-treated Fmr1 KO.
