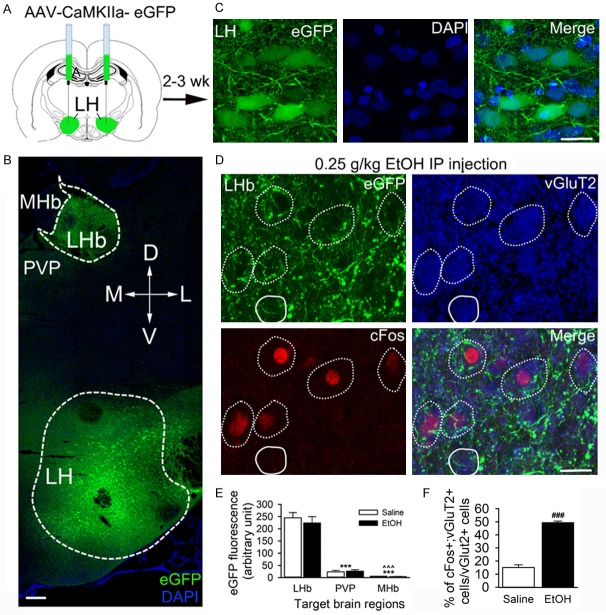
Figure 4.
Ethanol-activated LHb neurons receive inputs from the lateral hypothalamus (LH). AAV5-CaMKIIa-eGFP was infused into the LH of rats, 2-3 weeks before ethanol (0.25 g/kg, i.p.) or saline (1 ml/kg, i.p.). Brain slices containing the LH and the LHb were harvested 90 min post-i.p.-injections. (A) Schematic showed the AAV synaptic labeling tracing approach. (B) A confocal image of a coronal section illustrating the expression of AAV-eGFP in a brain slice containing both the LH and LHb (counterstained with DAPI). (C) High-resolution images of AAV-mediated expression of CaMKIIa-eGFP in LH neurons. (D) Confocal images demonstrated the overlap of ethanol-activated cFos+ (red) with vGluT2 staining (blue). Notably, a lot of eGFP+ (green) fibers were overlapped with the cell bodies (dotted white outlines), and a few vGluT2+ cells targeted by LH terminals were cFos- (white outlines). (E) Summary graph of LH-LHb eGFP fluorescence intensity in and around the LHb. MHb, medial habenula; PVP, posterior part of paraventricular thalamic nucleus; ***p < 0.001, vs. LHb; ^^^p < 0.001, vs. PVP. (F) Summary graph: ethanol treatment increased the percentage of cFos and vGluT2 co-localized cells/vGluT2 cells in LHb. ***p < 0.001, vs. Saline, n=5, unpaired t-test. Scale bar =200 μm (B), 20 μm (C & D).