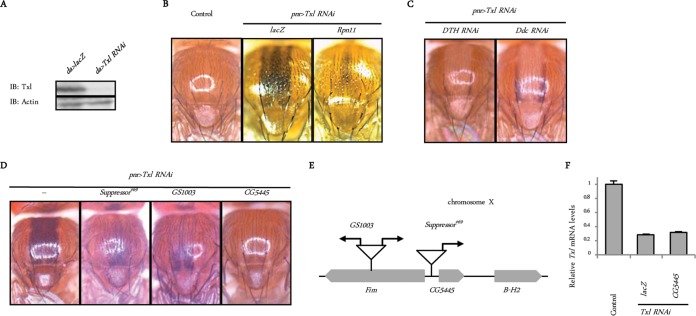
FIG 1.
Identification of CG5445 as a possible modifier of the UPS. (A) Confirmation of Txl knockdown. Txl was depleted in the whole body under the control of da-Gal4. Third-instar larvae were homogenized and subjected to immunoblot (IB) analysis with the indicated antibodies. Genotypes are UAS-lacZ/+; da-Gal4/+ and UAS-Txl RNAi/+; da-Gal4/+. (B) Appearance of Drosophila notum. Genotypes (from the left) are pnr-GAL4/+ (control), UAS-Txl RNAi/UAS-lacZ; pnr-GAL4/+, and UAS-Txl RNAi/UAS-Rpn11; pnr-GAL4/+. (C) Effect of downregulation of melanin synthesis on Txl knockdown-induced pigmentation. Genotypes are UAS-Txl RNAi/UAS-DTH RNAi; pnr-GAL4/+ and UAS-Txl RNAi/UAS-Ddc RNAi; pnr-GAL4/+. (D) GS lines and a CG5445 transgenic fly that suppress Txl knockdown-induced melanization. Genotypes (from the left) are Suppressor#69/+; UAS-Txl RNAi/+; pnr-GAL4/+, GS1003/+; UAS-Txl RNAi/+; pnr-GAL4/+, and UAS-Txl RNAi/UAS-CG5445; pnr-GAL4/+. (E) Schematic representation of the genomic locus on chromosome X where the GS vectors are inserted. Arrows represent directions of UAS sequences. (F) Txl was depleted under the control of the da-Gal4 driver. Since flies with Txl knockdown in the whole body exhibited developmental lethality during the pupal stage, flies were raised at 18°C until eclosion to repress GAL4 by GAL80ts, a temperature-sensitive repressor of GAL4, and then incubated at 29°C for 10 days to repress GAL80ts. Total RNAs of each genotype were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Genotypes (from the left) are tub-Gal80ts/UAS-lacZ; da-Gal4/+ (control), tub-Gal80ts UAS-Txl RNAi/UAS-lacZ; da-Gal4/+, and tub-Gal80ts UAS-Txl RNAi/UAS-CG5445; da-Gal4/+. Data are means and standard deviations of results from three experiments.