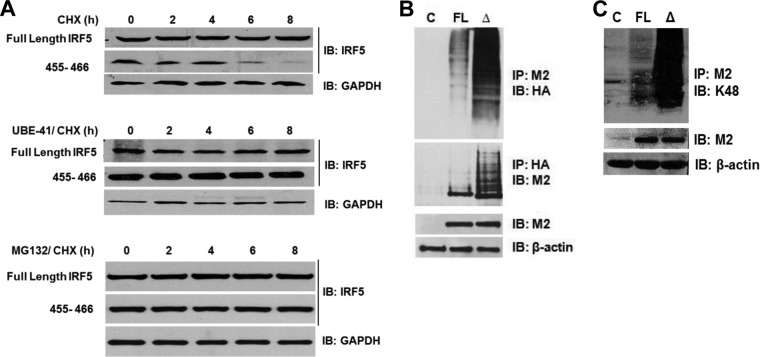
FIG 6.
IRF5 degradation is abrogated by the inhibition of ubiquitin activating enzyme 1 (E1) or the proteasome. (A) Plasmids encoding full-length IRF5 or the Δ455-466 mutant were transiently transfected into Hek 293T cells and treated with CHX or CHX plus UBE-41 (ubiquitin E1 inhibitor) or MG132 (proteasome inhibitor). The rate of IRF5 and GAPDH protein decay was examined by immunoblot analysis. Panels are labeled by treatment regimen. (B) Similar to that described for panel A except that the HA-Ub plasmid was cotransfected with plasmids encoding empty vector (lane C), full-length IRF5 (lane FL), or Δ455-466 mutant IRF5 (lane Δ) into Hek 293T cells to examine IRF5 ubiquitination. Reciprocal immunoprecipitations are shown by pulling down IRF5 (M2) or ubiquitin (HA). Levels of IRF5 and β-actin are shown in whole-cell lysates used for immunoprecipitations. (C) Similar to that described for panel B except that cells were not transfected with HA-Ub and the levels of IRF5 K48-linked ubiquitination were determined by immunoblotting M2 precipitates with anti-K48-linked polyubiquitination antibodies. Expression of IRF5 and β-actin in whole-cell lysates used for the immunoprecipitations is shown.