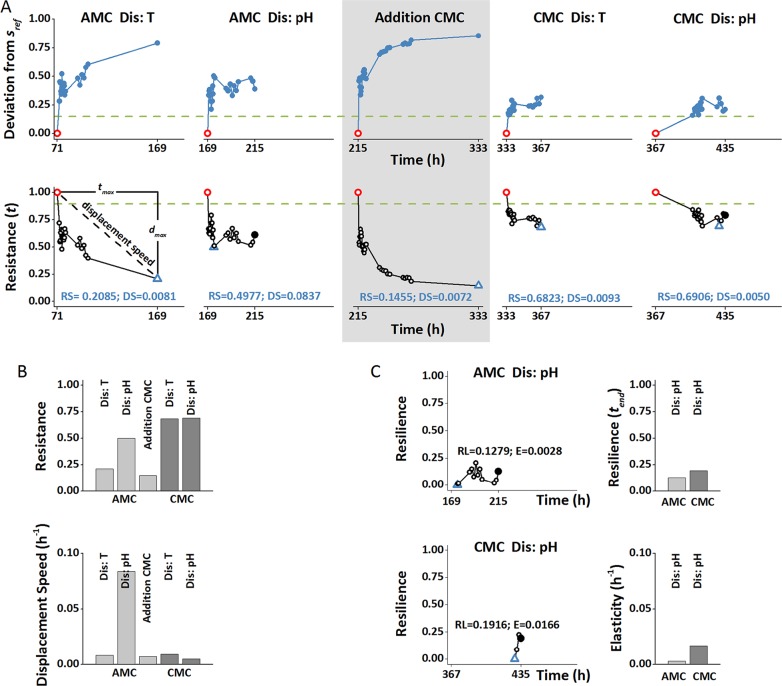
FIG 1 .
Response of microbial communities to disturbance events and stability properties of resistance, displacement speed, resilience, and elasticity (Table 1). A low-complexity member community (AMC) and, after addition (gray box), a complex community (CMC) were cultivated under the same conditions. Both the AMC and CMC structures were displaced in response to short-term temperature and pH disturbances (Dis: T and Dis: pH, respectively). (A) Deviation from the reference state (sref) (red circle), calculated as the Canberra distance, and resistance over time. Dashed horizontal green lines indicate the border of the reference space, blue triangles mark smax, and filled black circles mark send. The determination of resistance (RS) and displacement speed (DS) is shown as a dashed black line. (B) Comparison of the stability properties resistance and displacement speed across all disturbance experiments. (C) Comparison of the stability properties resilience and elasticity for disturbance experiments showing resilience (AMC Dis: pH and CMC Dis: pH).