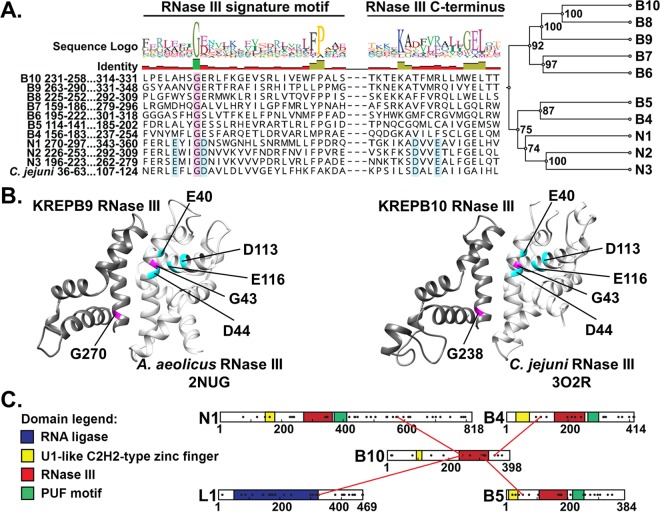
FIG 3 .
The RNase III domain identified in KREPB9 and KREPB10 conserves a structurally critical glycine residue in the signature motif. (A) Alignment of RNase III domain sequences from KREPB4- to -B10, KREN1 to -N3, and Campylobacter jejuni (GenBank accession number Q9PM40; PDB ID 3O2R). A total of 299 sequences from 35 kinetoplastid species and strains were aligned using MUSCLE. Only T. brucei sequences and the RNase III signature motif (C terminus) are shown here for clarity. Cyan shading indicates residues that aligned with those required for metal ion coordination and RNase III catalytic activity. These residues are conserved in the endonucleases KREN1 to -N3 but degenerate in KREPB4 to -B10. A universally conserved glycine is shown (shaded in magenta). An unweighted pair group method using average linkages phylogram of catalytic and noncatalytic RNase III domain-containing editosome proteins, inferred from analysis of the alignment described above, is shown. The frequencies (percentages) with which nodes were recovered in 1,000 bootstrap replications are shown. (B) Comparative modeling of KREPB9 (left) and KREPB10 (right) with the indicated bacterial RNase III crystal structures, which show critical placement of the conserved glycine residue. (C) Schematic of the location of cross-links of KREPB10 to other editosome proteins identified via CXMS. Identified cross-links fall in or near the RNase III domain.