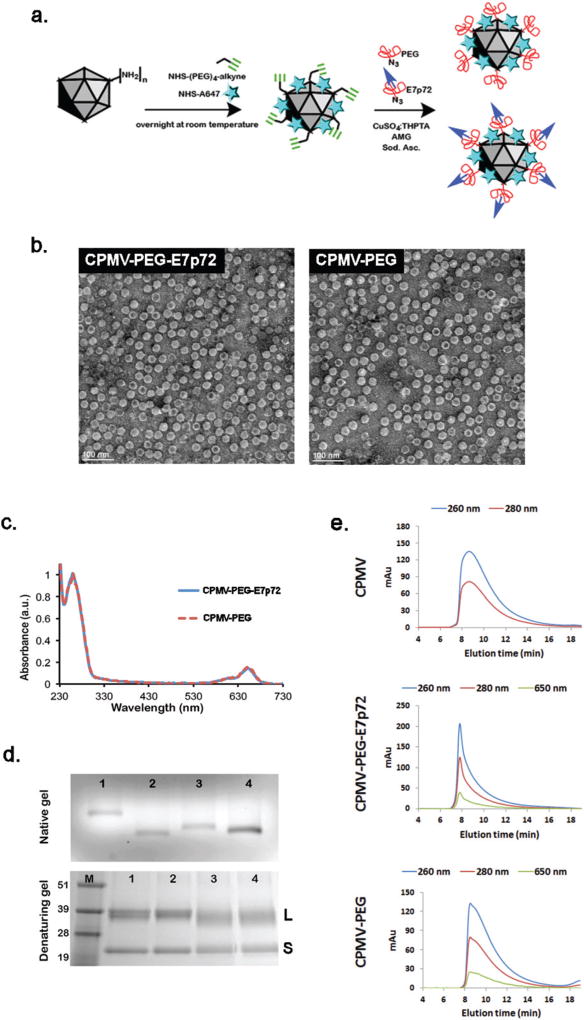
Fig. 4.
Synthesis and characterization of viral nanoparticles targeting EGFL7. (a) Schematic showing the two-step synthesis protocol employed for the modification of CPMV particles: (1) A647 and alkyne handles are introduced; (2) CuAAC chemistry is used to conjugate the PEG-E7p72 peptide or PEG molecules. (b) Transmission electron microscope images of CPMV-PEG-E7p72 or CPMV-PEG nanoparticle. Scale bar, 100 nm. (c) UV/visible spectra of CPMV-PEG-E7p72 confirming conjugation of ~25 NIR dyes per CPMV formulation. (d) Native (top panel) and denaturing (bottom panel) gel electrophoresis. The native gel was stained with ethidium bromide and imaged under UV light, while the denaturing gel was stained with Coomassie dye and imaged under white light. 1 = CPMV, 2 = CPMV-647-alkyne intermediate, 3 = CPMV-PEG-E7p72, 4 = CPMV-PEG. M corresponds to the molecular weight marker (molecular weights are indicated in kDa). (e) Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) of CPMV, CPMV-PEG and CPMV-PEG-E7p72 (1 mg mL−1; flow rate 0.5 mL min−1) using a Superose6 column on the ÄKTA Explorer chromatography system.