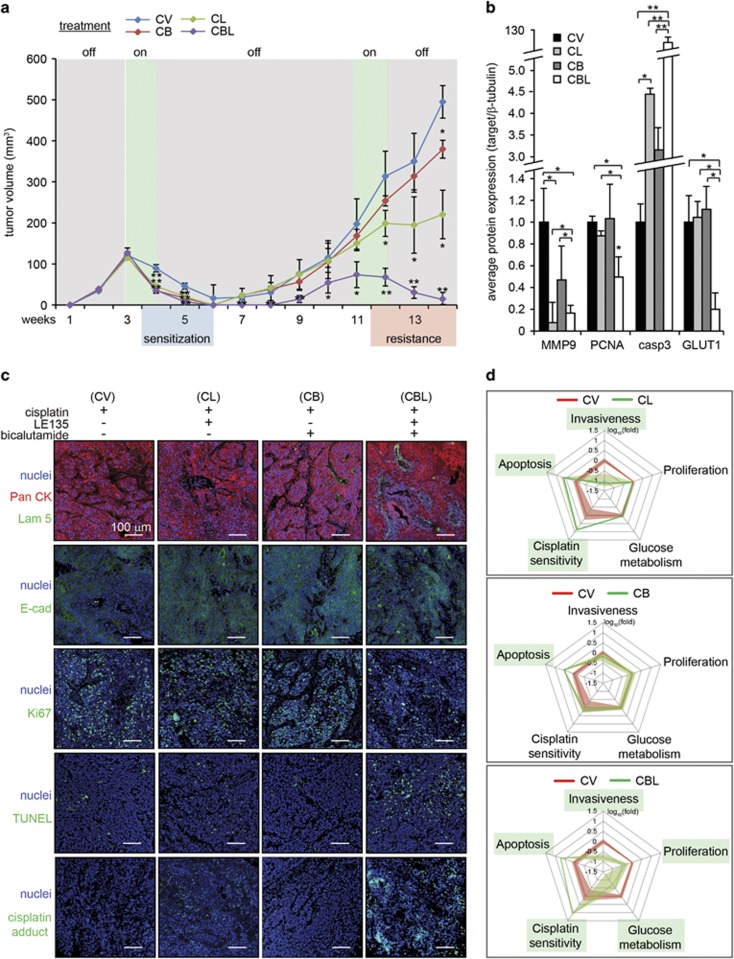
Figure 6.
Intratumoral injection of cisplatin increases the efficacy of combination therapies. (a) Tumor volume measurements in mice implanted with A-5RT3:CAF xenograft tumors (n=6 per experiment condition, two tumors per mouse) receiving intratumoral injections of 2 mg/kg cisplatin, alone (CV) or in combination with intraperitoneal injections of 5 mg/kg LE135 (CL), or 10 mg/kg bicalutamide (CB) or both (CBL). The treatments were administered on weeks 3 and 4, withdrawn from weeks 5–10 and resumed on weeks 11 and 12. (b) Densitometry measurements from zymogram for MMP2 and immunoblots of PCNA, caspase 3 and GLUT1 in mice that received intraperitoneal injections of NR ligands and intratumoral injections of cisplatin. β-Tubulin from the same samples was used as a loading and transfer control. Values are means±s.d. from n=3 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (c) Immunofluorescence staining for pan-cytokeratin (PanCK), laminin 5 (Lam 5), E-cadherin (E-cad), Ki67, TUNEL and cisplatin adducts in xenograft tumors of mice receiving intraperitoneal injections of NR ligands and intratumoral injections of cisplatin. Scale bar: 100 μm. (d) Multi-parametric evaluation of CAF NRs effect on SCC. Measured parameters from CV-treated tumors (red line) and combination therapies (CL, CB, CBL; green line) are superimposed. Shading represents the standard error of each parameter. Parameters significantly altered by combination therapies are boxed in green.