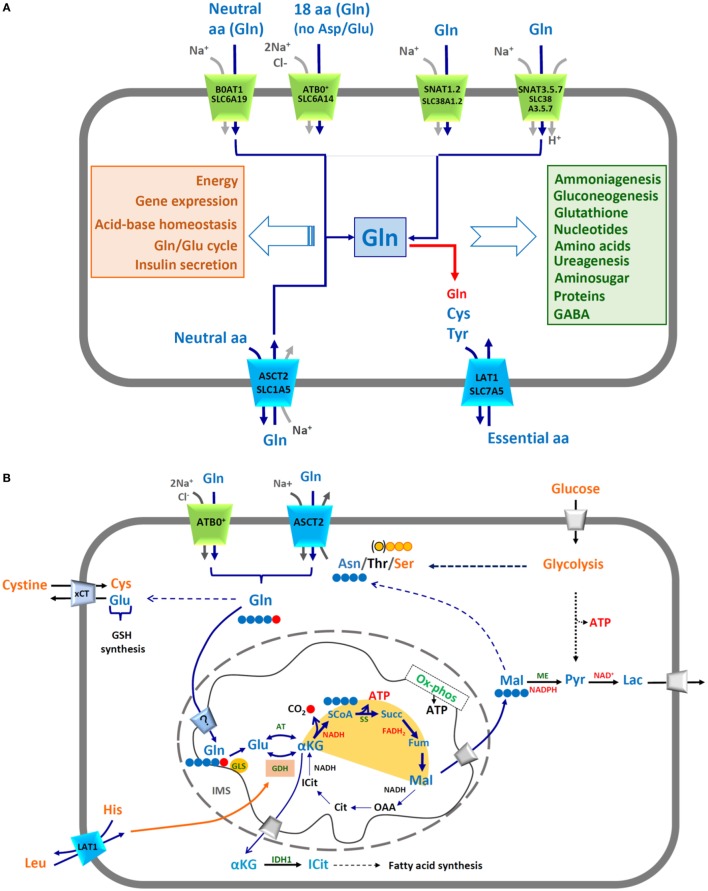
Figure 1.
(A) Membrane transporters of glutamine and mechanisms of transport. The shape of the transporters reflects their asymmetry in membrane. Transporters are indicated by both conventional and SLC names. Different colors highlight different transport modes: in green symporters, in blue antiporters. Arrows represent direction of transported amino acids (blue) and ion (grey) fluxes; red arrow indicates possible Glutamine exit via LAT1 (SLC7A5). In the orange box, the list of cell pathways in which Glutamine is involved; in the light green box, the list of molecules synthesized from Glutamine. (B) Mitochondrial and cytosolic pathways responsible for energy production from Glutamine. In the scheme, Glutamine (Gln, blue) uptake occurs via membrane transporters ATB0,+ and ASCT2 through a sodium coupled process. The pathways are indicated as solid or dotted (in the case of multistep pathways) arrows (in blue those related to Glutamine, in black those involved in other pathways). Carbon atoms of Gln are depicted in blue–red filled circles; Gln enters mitochondria via an inner membrane transporter whose existence is still questionable (?): it could be a Glutamine or a Glutamate transporter depending on the actual sub-localization of Glutaminase enzyme (GLS). Carbon atom derived from Gln and released as CO2 is indicated in red, carbon skeleton of Malate and Asparagine (Asn) in blue, carbon skeletons of Serine (Ser) in orange circled in red and of Threonine (Thr) in orange circled in black. The truncated form of TCA is highlighted by a yellow hemicycle. ATP and reducing equivalent molecules produced by Glutamine metabolism are indicated in red. Leucine enters through LAT1 and allosterically regulates GDH in the orange box. Some metabolic pathways are indicated by names: GSH synthesis, fatty acid synthesis, Glycolysis, OX-phos. Membrane transporters of lactate and glucose in grey, xCT in light blue. Enzymes highlighted: GLS, Glutaminase; GDH, Glutamate dehydrogenase; AT, aminotransferases; SS, succinylCoA synthetase; ME, malic enzyme; IDH1, isocitrate dehydrogenase. Amino acids and other molecules involved in glutamine pathways (azure): Glu, Glutamate; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; ICit, isocitrate; SCoA, succinyl coenzyme A; Succ, succinate; Fum, fumarate; Mal, malate; OAA, oxaloacetate; Cit, citrate; Pyr, pyruvate; Lac, lactate.