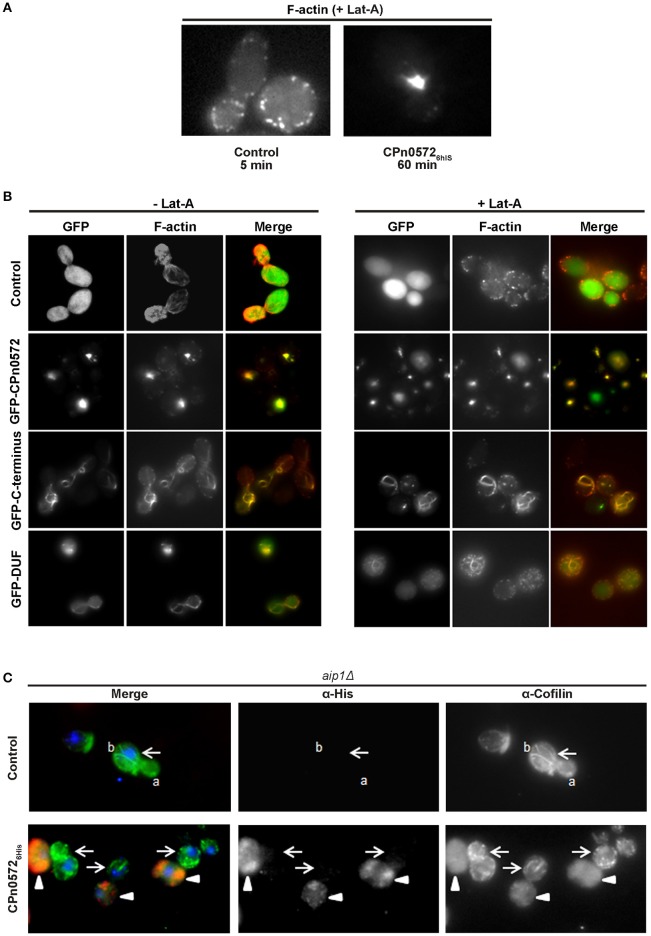
Figure 6.
CPn0572 and its C-terminal segment stabilize F-actin and displace cofilin from F-actin in yeast in vivo. (A) GFP- (control) or GFP-CPn0572-expressing cells were treated with Lat-A (+ Lat-A) for the indicated times, and stained for F-actin. (B) Actin cytoskeleton patterns in yeast cells expressing full-length CPn0572 or its deletion variants before and after treatment with Lat-A. Yeast cells expressing GFP (control), GFP-CPn0572, GFP-C-terminus or GFP-DUF were first grown to mid-log phase in inducing medium, exposed to DMSO alone (– Lat-A) or Lat-A (final concentration 2.5 μM) in DMSO (+ Lat-A) for 1 h, then fixed and stained with rhodamine-phalloidin to visualize F-actin, and examined using an Axiovert 200 microscope (Carl Zeiss). (C) In aip1Δ yeast cells carrying the empty vector (control), cofilin (green) localizes to actin patches and cables (marked by a and b, respectively). In cells expressing CPn05726His (red), cofilin is diffusely distributed (arrowheads), while non-expressing cells retain distinct cofilin patches and cables (arrows). See also Figure S4.