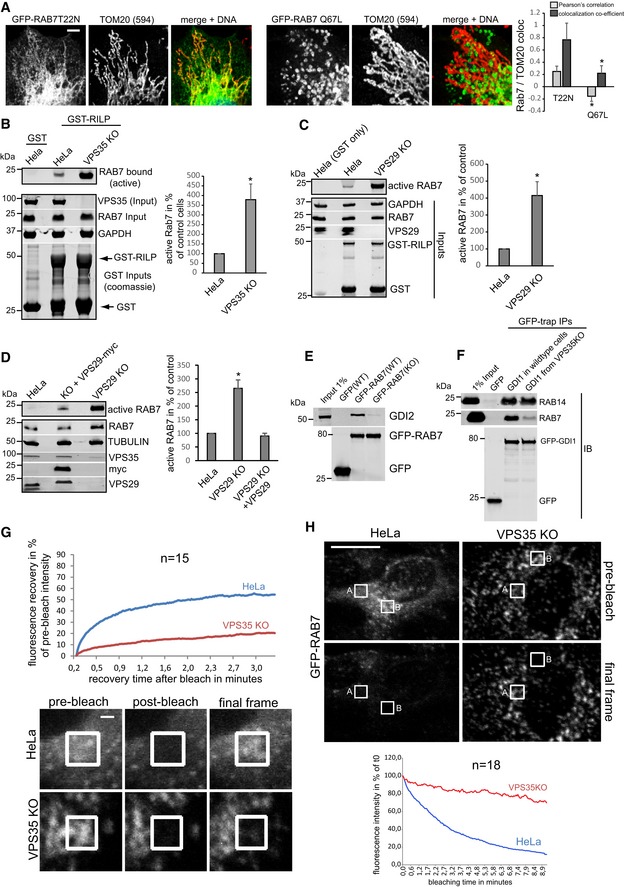
GDP‐locked (inactive) GFP‐RAB7‐T22N and GTP‐locked (constitutively active) GFP‐RAB7‐Q67L were lentivirally expressed in RAB7 KO cells and co‐stained with the mitochondrial marker TOM20 (red). Co‐localization was analyzed over two independent experiments with 10 images each.
Lysates from parental HeLa cells and clonal VPS35 KO cells were probed with immobilized GST‐RILP protein, and GST‐RILP‐bound (active) RAB7a was detected and quantified by fluorescent Western blotting across three independent experiments.
Lysates from parental HeLa cells and clonal VPS29 KO cells were probed with immobilized GST‐RILP protein, and GST‐RILP‐bound (active) RAB7a was detected and quantified by fluorescent Western blotting across three independent experiments.
Lysates from parental HeLa cells and clonal VPS29 KO cells and VPS29 KO cells with lentivirally re‐expressed VPS29‐myc were probed with immobilized GST‐RILP protein, and GST‐RILP‐bound (active) RAB7a was detected and quantified by fluorescent Western blotting across three independent experiments.
Lentivirally expressed GFP‐RAB7 was precipitated from parental and from VPS35 KO cells, and the precipitates were analyzed for the presence of the endogenous RAB‐chaperone GDI2.
Lentivirally expressed GFP‐GDI1 was precipitated from parental and from VPS35 KO cells, and the precipitates were analyzed for the presence of endogenous RAB14 and endogenous RAB7a.
GFP‐RAB7 was transduced into parental HeLa cells and VPS35 KO cells and analyzed for its mobility/membrane turnover using FRAP imaging in live cells. The recovery kinetics were obtained by averaging 15 FRAP recoveries acquired in two independent experiments.
GFP‐RAB7 was transduced into parental HeLa cells and VPS35 KO cells and analyzed for its mobility/membrane turnover using FLIP imaging in live cells. The depletion kinetics (in area A, as indicated) were obtained by averaging 18 FLIP depletions acquired in two independent experiments.
‐test of the respective condition compared to the control cells.