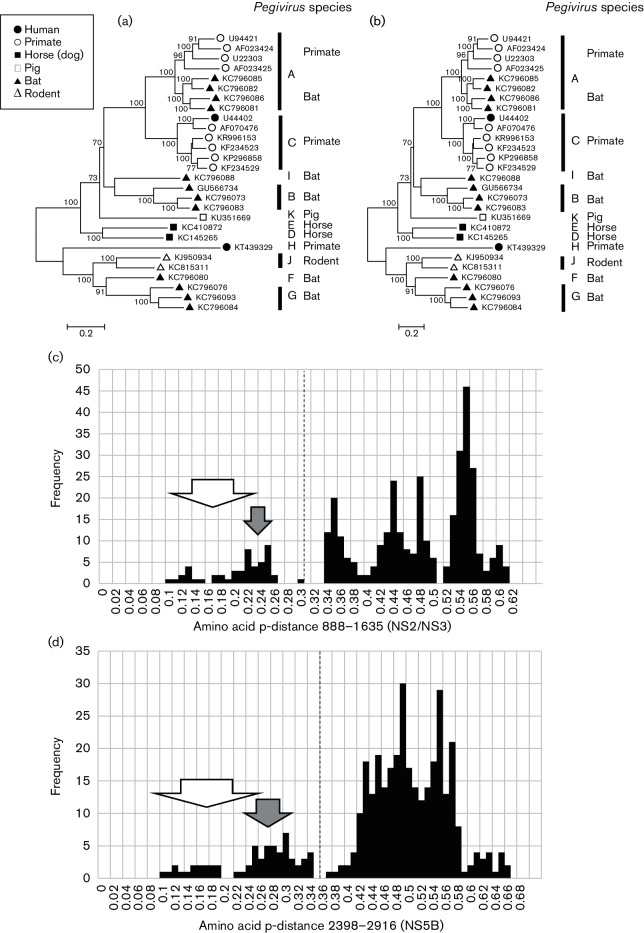
Fig. 4.
Analysis of Pegivirus conserved regions. Maximum-likelihood trees were produced using mega6 for (a) amino acid positions 888–1635 using the Le and Gascuel model with frequencies and a gamma distribution of variation with invariant sites, and for (b) amino acid positions 2398–2916 using the Le and Gascuel model with a gamma distribution of invariant sites. Branches observed in >70 % of bootstrap replicates are indicated. Frequency histograms of amino acid p-distance between Pegivirus sequences in the region 888–1635 (c) and the region 2398–2916 (d) Amino acid p-distances between Pegivirus C sequences derived from different primate species are indicated by an open arrow, while those between primate- and bat-derived Pegivirus A sequences are indicated by a shaded arrow. The distance that demarcates different species is indicated by a broken line.