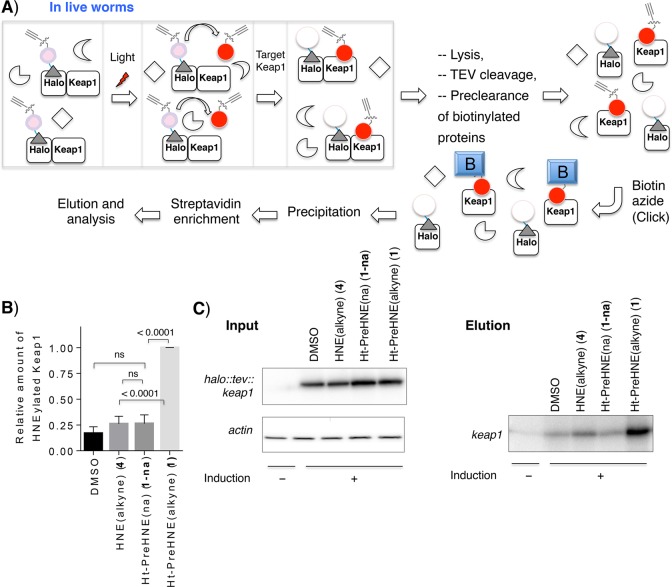
Figure 3.
T-REX concept of proximity-targeted on-demand release of HNE in situ under electrophile-limited conditions that selectively HNEylate Keap1 protein expressed in live C. elegans. (A) Schematic of optimized biotin-Click pull-down conditions compatible with the C. elegans lysate (readout C, Figure 1). “B” indicates biotin. See the methods in the Supporting Information for details. (B) The inset shows quantitation of the extent of HNEylated Keap1 under the indicated conditions [n ≥ 5 independent biological replicates (Figure S5); errors indicate the standard error of the mean]. Bulk HNE exposure and T-REX give different extents of HNEylation on Keap1, suggesting that uptake/metabolism is a more significant variable in living model organisms than in living cells where HNEylation efficiencies are largely found to be comparable between the two conditions.3 (C) Representative data set for input and elution samples. Actin serves as a loading control. Induction designates heat shock for transgene expression. Also see Figure S5.