Fig. 7.
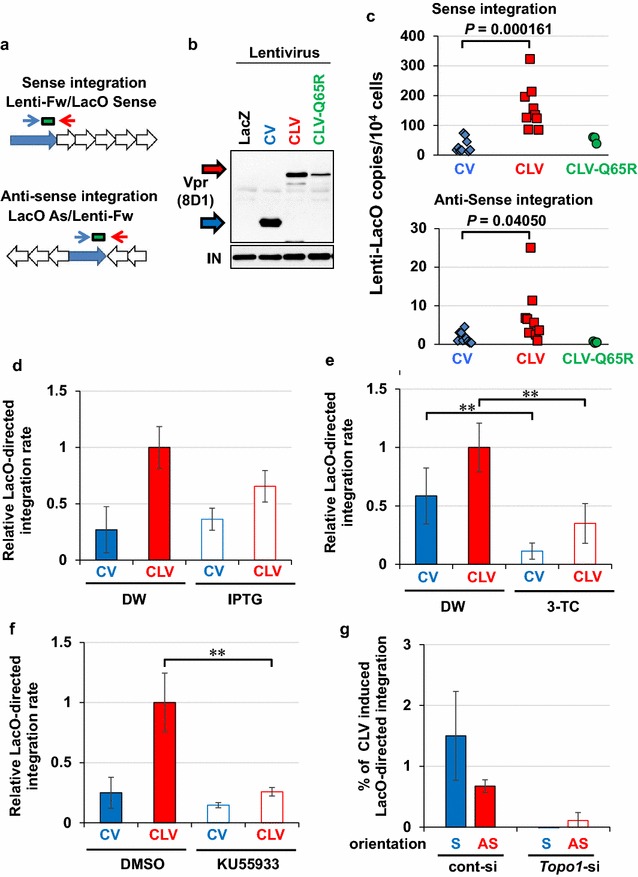
Proviral DNA integration in Vpr-accumulated sites. a Schematic of LacO-directed integration of proviral DNA. The qPCR analysis of the copy number of LacO-integrated proviral DNA was performed using PCR primers targeting the 3′-LTR (blue arrow) and LacO repeat (red arrow). The green box indicates the position of the TaqMan probe for the 3′-LTR (nucleotide sequence is shown in Additional file 20: Table S3). b Production of lentiviral particles with CV, CLV, and CLV-Q65R. Integrase (IN) was detected as an internal control. LacZ-coding lentivirus (LacZ) was included as a negative control. c Site-specific integration of proviral DNA. CV, CLV, and CLV-Q65R incorporated lentivirus was infected into U2OS/2-6-3 cells and subjected to qPCR analysis (Fig. 7a) at 2dpi (n = 9, 9, 3 for CV, CLV, and CLV-Q65R, respectively). Similar infectivity of each virus was confirmed by colony-formation assay (Additional file 12; Figure S11). d Effects of LacO/LacR inhibition on site-specific integration of proviral DNA. Cells were pretreated with IPTG (15 mM, 1 h) prior to the lentivirus infection. Error bars indicate ± SEM. Data were obtained from more than three independent experiments. e A reverse transcriptase inhibitor blocked the infection. Cells were pretreated with 3-TC (50 μM, 1 h) prior to lentivirus infection. **P < 0.05. f Site-specific integration of proviral DNA depended on ATM activity. ATM inhibitor, KU55933 (10 μM) was added to culture medium 1 h before infection. g Topo1 is important for site-specific integration of proviral DNA. A U2OS/2-6-3 subclone transduced with pCAL-loxP-CLV (263/loxP-CLV) was infected with Cre- or LacZ-expressing adenovirus for 2 days under down-regulation of Topo1. The cells were then infected with NL4-3/D64A/R− virus and subjected to qPCR analysis at 2dpi. The overall integration rate was quantitated by Alu-gag two-step nested qPCR (Additional file 11: Figure S10) to estimate the percentage of LacO-directed integration. S sense integration, AS anti-sense integration
