Figure 2.
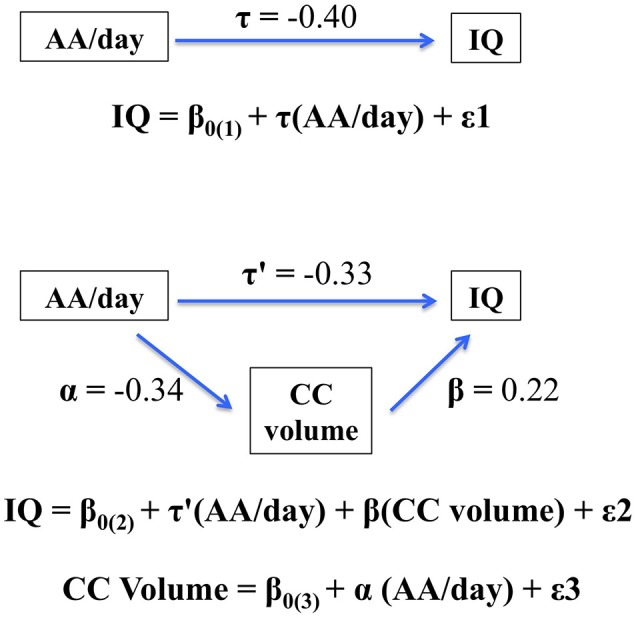
Path model showing partial mediation of the association between AA/day and IQ by corpus callosum (CC) volume. The figure shows that the effect of prenatal alcohol exposure on IQ is partially mediated by the fetal alcohol-related corpus callosum volume reduction. When CC size was added in Step 2 of the regression analysis, the effect of AA/day on IQ was reduced from −0.40 to −0.33, a reduction that was statistically significant, Clogg (t = −2.86, p < 0.01).
