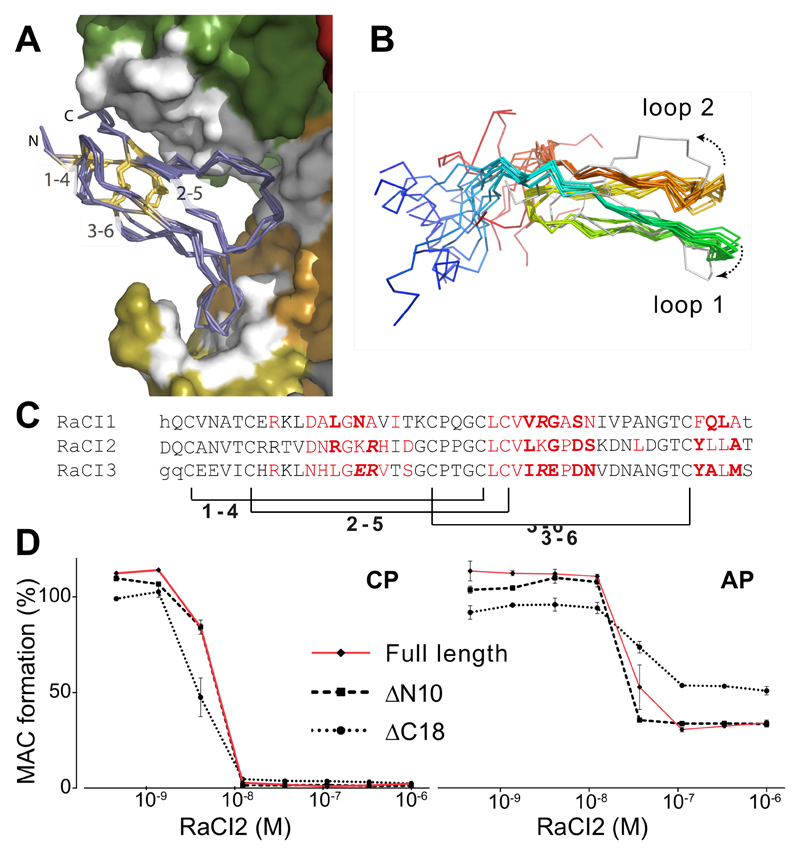
Figure 4. The structurally conserved core of the RaCI family members is sufficient for activity.
(A) Overlay of RaCI1, 2 & 3 in the C5 binding site (colored as in Fig. 3D). The RaCI proteins are shown as alpha carbon traces with the N- and C-termini and disulphide bonds highlighted. (B) An ensemble of the 10 lowest energy NMR structures of RaCI2 (colored blue to red from N- to C-termini) shows two conserved loops and highly mobile N- and C-terminal regions. The ensemble is overlaid on the structure of RaCI2 (grey) taken from the C5-OmCI-RaCI2 complex. (C) Alignment of RaCI1-3 ordered core residues. Residues that were not seen in the electron density are in lower case. Residues that make van der Waals interactions in red, hydrogen bonds in bold and salt bridges are in italics. Brackets indicate conserved disulphides. (D) Elisa-based activation assay (CP – classical pathway, AP – alternative pathway) to test inhibitory effect of RaCI2 mutants that lack N- and C-termini (lacking 10 and 18 amino acids respectively, see Figure 1A for truncation sites) Error bars, s.e.m. (n = 3 technical replicates).