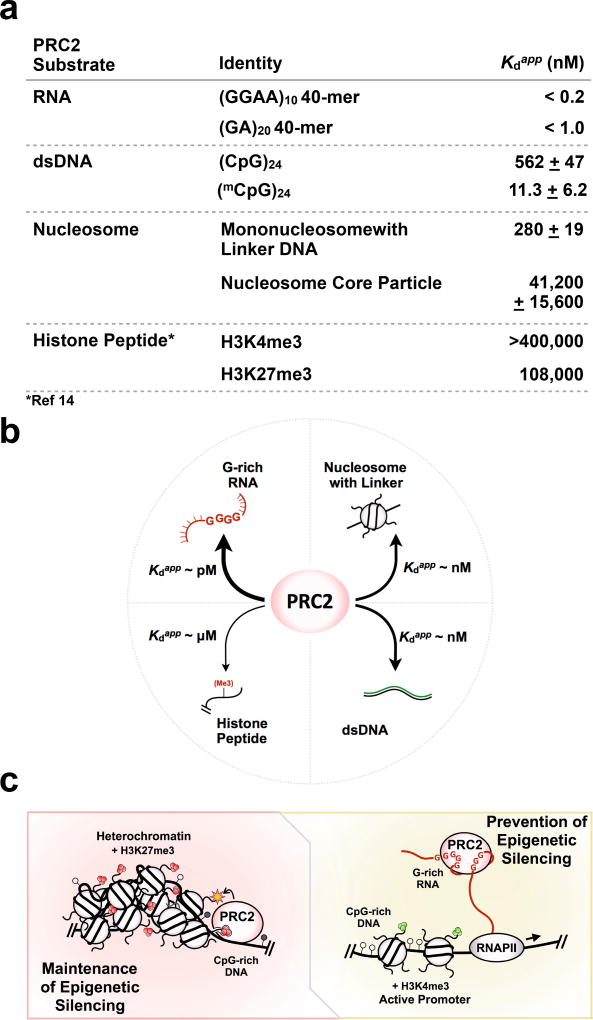
Figure 7.
A model for PRC2-chromatin-RNA interactions and regulation of epigenetic silencing. (a) A summary of relative PRC2 binding to RNA, DNA, nucleosomes, and histone peptides. All Kdapp values were determined by EMSA under the same conditions, in the absence of tRNA competitor, with the exception of the literature Kd values for histone peptide binding14 which were determined by ITC. (b) A comparison of binding affinity of PRC2 to various substrates reveals that PRC2 binds RNA >> nucleosomes with linker DNA ≈ DNA >> histone tails. (c) Model includes (left) maintenance of epigenetic silencing, where high-affinity DNA-binding modules of PRC2 allow the complex to preferentially bind nucleosome-free regions and methylate an adjacent nucleosome, and (right) prevention of epigenetic silencing, where RNA binding suppresses H3K27 methylation by interfering with the DNA binding required by PRC2 to bind chromatin. Heterochromatin is characterized by H3K27me3 marks and dense nucleosome packing. Active promoters feature H3K4me3 marks. CpG islands featuring unmethylated (open circles) and methylated (filled circles) CpG dinucleotides in gene promoter regions may serve as a conduit for PRC2 targeting. Even though the model may be an oversimplification, it provides an interpretation of how epigenetic silencing could be switched on-and-off under certain chromatin states, as deduced from our quantitative study of PRC2 substrate binding.