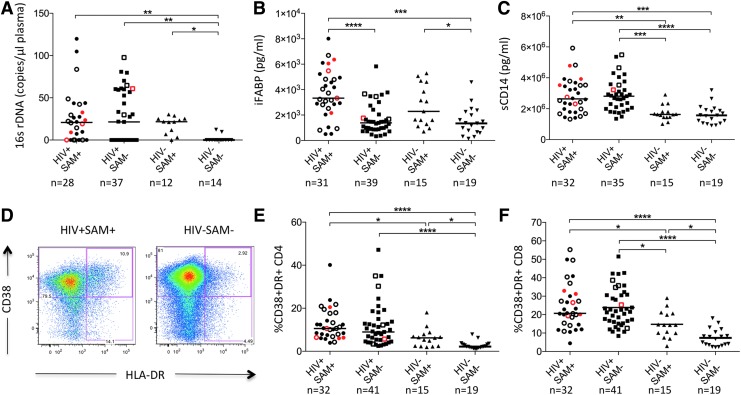
FIG. 1.
Plasma biomarkers and immune activation by study group at baseline. (A–C) Plasma levels of 16sDNA (A), iFABP (B), and sCD14 (C) in children stratified by HIV status and presence of SAM at baseline. Open symbols indicate active tuberculosis disease; red symbols indicate children that passed away during the study period. Medians are shown as horizontal bars. (D) Representative CD4+ T cell immune activation FACS data from an HIV-positive child with severe acute malnutrition (HIV+SAM+, left) and a healthy control (HIV−SAM−, right). (E, F) Activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in children stratified by HIV status and nutritional state. Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA with Dunn's correction for multiple comparisons was used to determine statistical significance (*p < .05; **p < .01; ***p < .001; ****p < .0001). iFABP, intestinal fatty acid-binding protein; SAM, severe acute malnutrition.