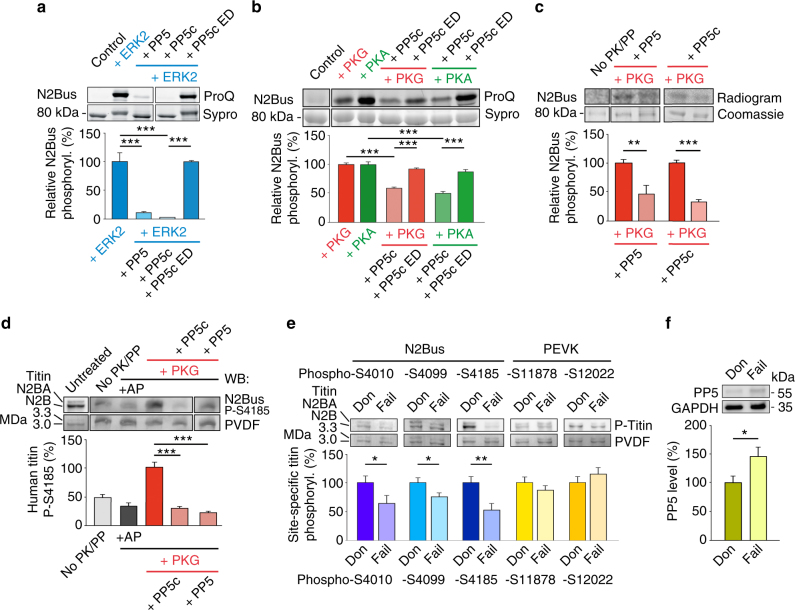
Fig. 3. PP5 dephosphorylates recombinant and endogenous human N2Bus.
a, b ProQ Diamond phosphoprotein vs. Sypro Ruby total protein stain of human recombinant N2Bus phosphorylated (in presence of ATP) by ERK2 (a), catalytic subunit of PKA (b), or cGMP-activated PKG (b), and effect of human recombinant full-length PP5, PP5 catalytic subunit (PP5c), or enzymatic dead (ED) PP5c mutant H304A on phosphorylation. ‘Control’ is recombinant construct but no ATP/enzyme. n = 5. c 32P-ATP autoradiography using N2Bus phosphorylated by cGMP-activated PKG and dephosphorylated by PP5 or PP5c. ‘No PK/PP’ is control in presence of 32P-ATP, but no enzyme. n = 4. d Western blot (WB) of permeabilized human (donor) heart tissue treated with various enzymes, as follows: alkaline phosphatase (AP), cGMP-activated PKG, then PP5 or PP5c. Detection of titin phosphorylation with phospho-specific antibody to P-S4185 in human N2Bus. PVDF was coomassie-stained to reveal loading on gel. WB signals were normalized to PVDF signals. n = 4. e Site-specific phosphorylation of residues within N2Bus and PEVK titin regions by western blot in myocardial tissue from human donor (Don) and end-stage failing (Fail) hearts (n = 10/group). Detection with phospho-specific antibodies to P-S4010, P-S4099, P-S4185, P-S11878, and P-S12022 in the human titin sequence. WB signals were normalized to PVDF signals. f Mean PP5 expression in human donor vs. end-stage failing hearts (n = 10/group). In a–f, bar graphs show relative phosphorylation indexed to the respective phosphorylated controls. Data are mean ± s.e.m.; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, by two-tailed Student’s t-test or Holm-Sidak method