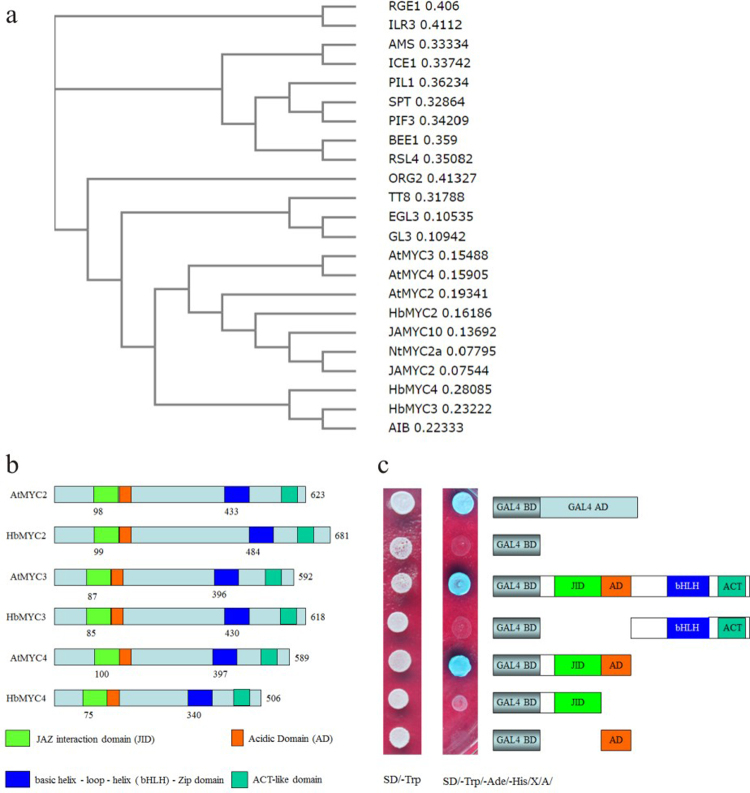
Figure 2.
Comparison of the MYC genes of Hevea brasiliensis and other bHLH-type transcription factors. (a) Phylogenetic tree of the deduced amino acid sequences of HbMYCs and other plant bHLH proteins. The phylogenetic tree was generated based on the alignment of the full-length deduced amino acid sequences of 23 bHLH proteins. Alignment was performed and the phylogenetic tree was constructed by Clustal Omega (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/), with the default settings. (b) Domain comparisons between HbMYCs and AtMYCs, JAZ-interacting domains (JIDs), acidic domains (ADs), basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-zip domains and ACT-like domains were included. C. Transcriptional activity analysis of the different domains of HbMYC3 proteins. Full-length or attenuated fragments of HbMYC3 were inserted into a pGBKT7 vector, after which the vectors were transferred into Y2HGold yeast strains and then plated on SD/-Trp/-Ade/-His/X-α-gal/AbA media.