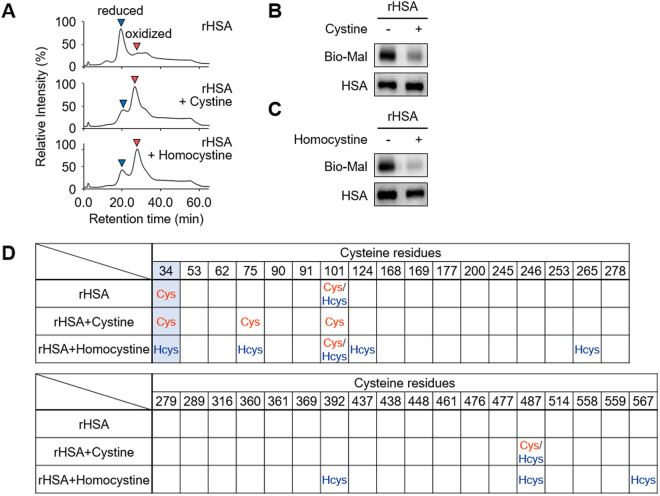
Figure 6.
S-Thiolation of rHSA by the treatment of cystine and homocystine. rHSA (150 μM) and cystine or homocystine (300 μM) were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 6.7) containing 0.3 M NaCl for S-thiolation of HSA. (A) HPLC chromatograph of rHSAs. rHSA (upper) and cystine (middle) or homocystine (lower) treated rHSA was analyzed by anion-exchange chromatography by monitoring the excitation at 280 nm and emission at 340 nm. (B) and (C) Detection of free cysteine residue. rHSA and cystine (B) or homocystine (C) treated rHSA were labeled with biotin-maleimide and subjected to non-reducing SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis. (D) Identification of S-thiolated cysteine residue of cystine or homocystine treated rHSA.