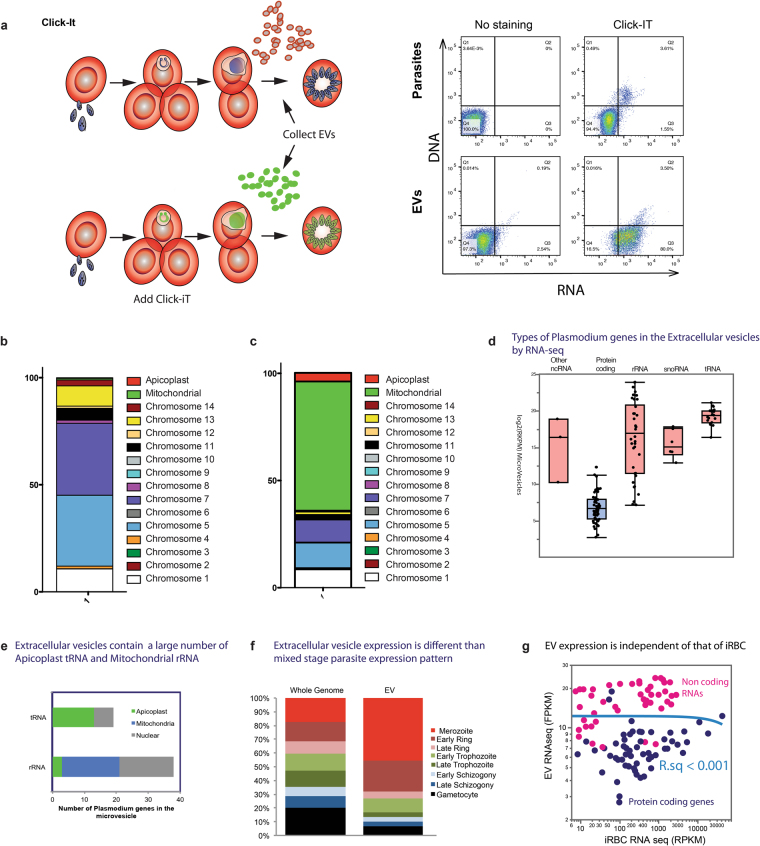
Figure 5.
EVs contain plasmodial RNAs. (a) Quantification of P. falciparum RNAs transferred to EVs. Infected RBCs were labeled with Click-It RNA Alexa Fluor 488. After 30 h. of incubation, EVs were collected and EU incorporation was analyzed by Flow Cytometry. (b) Distribution of the reads mapped to the P. falciparum genome according to the corresponding chromosomes. (c) Distribution of the reads mapped to the P. falciparum according to the size of the chromosome. (d) Types of Plasmodium genes in the EVs by RNA-Seq. (e) Extracellular vesicles contain a large number of Apicoplast tRNA and Mitochondrial rRNA. (f) RNA expression is different in EVs than mixed stage parasite expression pattern. (g) EV RNA composition is different that of iRBC. The expression levels shown by RNAseq of EV has no detectable correlation with that of steady state iRBC, showing that EV is not merely a smaller form of iRBC. Neither parametric (Pearson’s R) nor parametric correlations (Kendell’s tau) analysis detected correlation between EV and iRBC at any time points with correlation larger than 0.001. The X-axis shows the average steady state RNA expression levels.