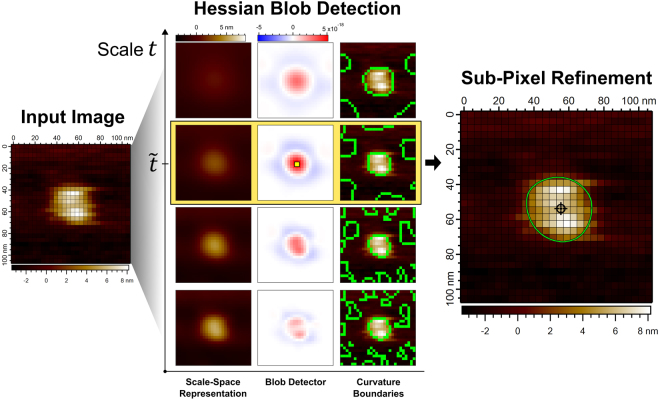
Figure 3.
Visual demonstration of the Hessian blob algorithm applied to an image of a translocase complex (SecYEG/SecA)41 with lateral pixel resolution 3.9 nm. From an input image, the scale-space representation is computed by discrete Gaussian smoothing, producing a stack of images indexed by the scale t, shown on the vertical axis. Differentiation and normalization yields , the blob detector, also a stack of images indexed by the scale t. Maximization of in space and scale yields a scale-space maximum, highlighted by the yellow pixel, giving the blob center point in scale-space and selecting scale . as the scale of the blob. In the third column, zero-crossings of the Gaussian curvature K are illustrated at different scales by green lines overlaid on the original image. Zero-crossings at scale , the scale of the detected blob, are used to define the Hessian blob boundary. Sub-pixel refinements to the blob center point and boundary are finally computed, with the sub-pixel precise center point marked by a crosshair and boundaries computed to twenty times the lateral pixel resolution (0.20 nm).