Figure 1.
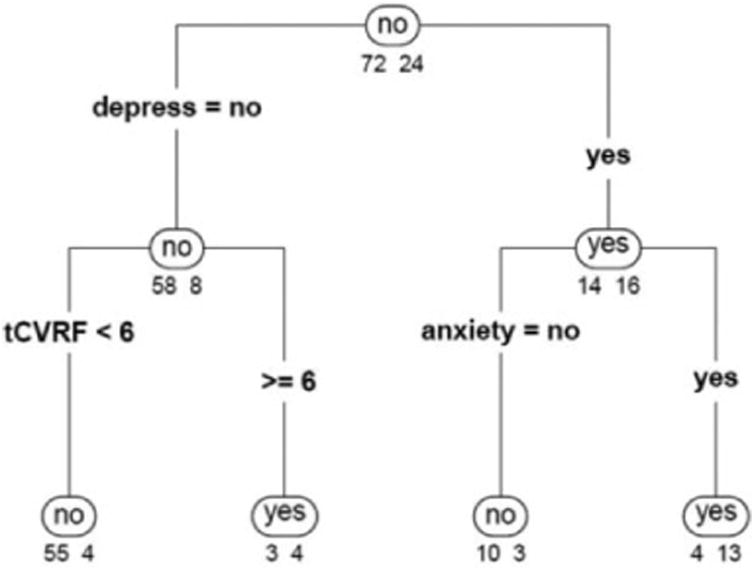
Classification tree categorizing patients with and without subjective memory changes using demographic and health characteristics (age, gender, education, depression, anxiety, and number of vascular risk factors). The numbers below each node indicate the proportion of patients with (right) and without (left) subjective memory changes for that classification outcome. For example, the “.88/.12” values on the left branch in the second level indicate that the majority of participants without symptoms of depression did not endorse subjective memory changes (88%), compared to a small proportion of those who did so (12%). depress indicates depression; tCVRF, total number of vascular risk factors.
