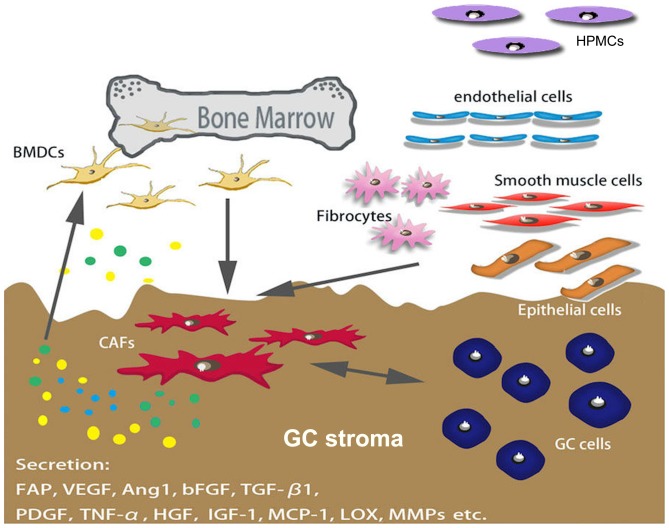
Figure 1.
Origination of CAFs in GC. Numerous types of cells are able to differentiate into CAFs, including BMDCs, smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, fibrocytes and epithelial cells. BMDCs are a major source of CAFs. Several factors secreted by cancer cells mediate the differentiation of CAFs, and certain markers (including α-smooth muscle actin, FAP and PDGF receptor α/β) have been used to distinguish CAFs from other types of fibroblasts. CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; GC, gastric cancer; BMDCs, bone marrow-derived cell; FAP, fibroblast activation protein; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; HPMCs, human peritoneal mesothelial cells; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; Ang1, angiopoietin 1; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor β1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; LOX, lysyl oxidase; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases.