Figure 1.
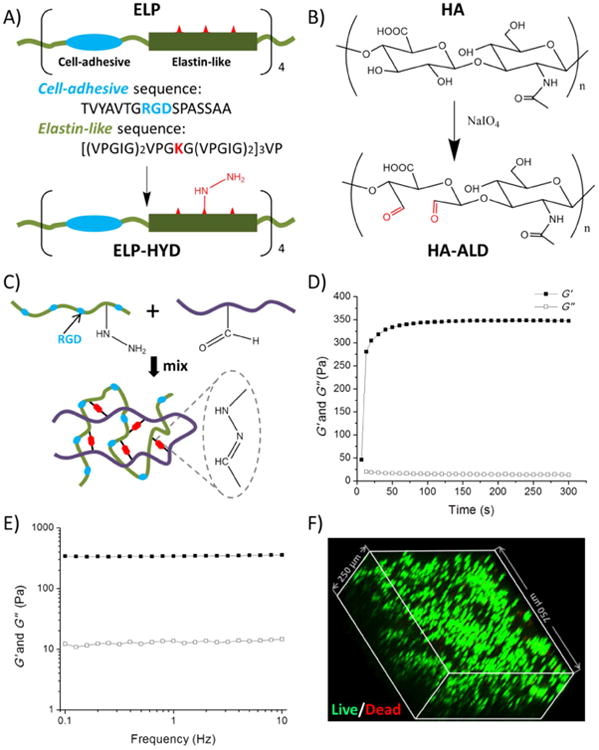
Design and characterization of protein hydrogels for 3D cell encapsulation. (A) Elastin-like protein (ELP) was designed with four modular repeats of cell-adhesive (blue) and structural elastin-like (green) sequences. Lysine residues (red) were used to generate hydrazine-modified ELP (ELP-HYD). (B) Synthesis of aldehyde-modified hyaluronic acid (HA-ALD). (C) ELP-HA hydrogel is formed via reaction between hydrazines on ELP-HYD and aldehydes on HA-ALD to form dynamic covalent hydrazone linkages. (D & E) Rheological characterization of ELP-HA (1.8 wt%, 1.5 wt%) hydrogel during (D) an oscillatory time sweep at 25 °C to demonstrate onset of gelation and (E) an angular frequency sweep at 37 °C to demonstrate gel stability at physiological conditions. Storage moduli (G′) are shown with filled symbols and loss moduli (G″) are shown with empty symbols. (F) Chondrocytes demonstrated round morphology and high viability after encapsulation in 3D ELP-HA hydrogels, as shown by confocal imaging of Live/Dead staining.
