Figure 5. AMPK promotes BCL6 up-regulation, both in the presence or absence of glycolysis.
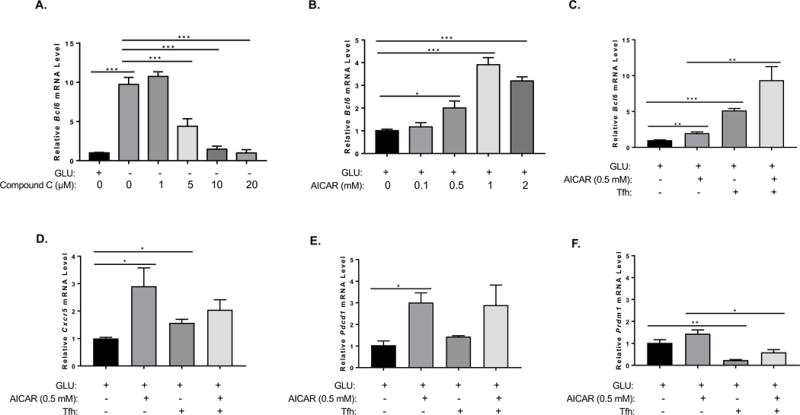
(A, B) Naïve CD4+ T cells isolated from C57BL/6 mice were cultured with complete media for 48 h on anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 coated wells. T cells were collected and washed once with PBS and cultured under complete (GLU+) or glucose (GLU-) deprivation medium for another 48 h on anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 coated plate. Relative mRNA expression was determined by QPCR. (A) Different doses of Compound C were added to cells for the last 24 h of re-stimulation culture. Bcl6 gene expression from isolated naïve CD4+ T cells cultured under complete or glucose deprivation medium with or without the addition of Compound C during re-stimulation (n=3, mean ± SEM). (B) Different doses of AICAR were added to cells for the 48 h of re-stimulation culture. Bcl6 gene expression from isolated naïve CD4+ T cells cultured under complete medium with or without the addition of AICAR during re-stimulation. Data are representative of two independent experiments with similar results. (C-F) Naïve CD4+ T cells isolated from C57BL/6 mice were cultured with complete media for 72 h on anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 coated wells, in medium alone or Tfh conditions (IL-6+IL-21, plus anti-IL-2, IL-2Ra, anti-IL2Rb, anti-TGFb, anti-IL-4, anti-IFNg), with and without AICAR. Cells were harvested for RNA isolation and gene expression analysis by QPCR for the indicated genes. (n=3, mean ± SEM). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA).
