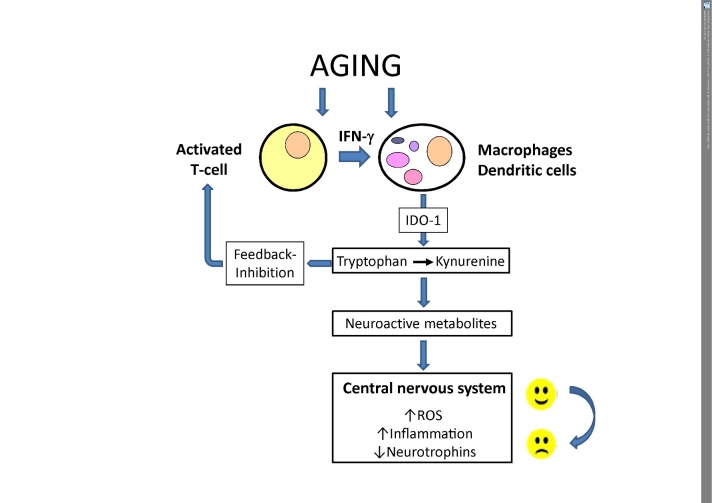
Figure 2. The induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) by aging.
The process of aging involves pro-inflammatory pathways which include activation of the T-cell-macrophage axis in the framework of the cell-mediated (Th1-type) immune response in which the formation of Th1-type cytokine interferon-γ (IFN-γ) is of utmost relevance. IFN-γ stimulates a broad spectrum of biochemical pathways that are directed to stop unwanted growth of pathogens or malignant cells. Among them, the conversion of essential amino acid tryptophan to kynurenine is a key element, which on the one hand is involved in a feedback inhibition of T-cell activation via regulatory T-cells and thus immunosuppressive. On the other hand, the catabolites generated by this strategy can impact on the central nervous system when neuroactive compounds accumulate and pro-inflammatory cascades including the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) interfere with neuroendocrine signaling, which controls mood and behavior.