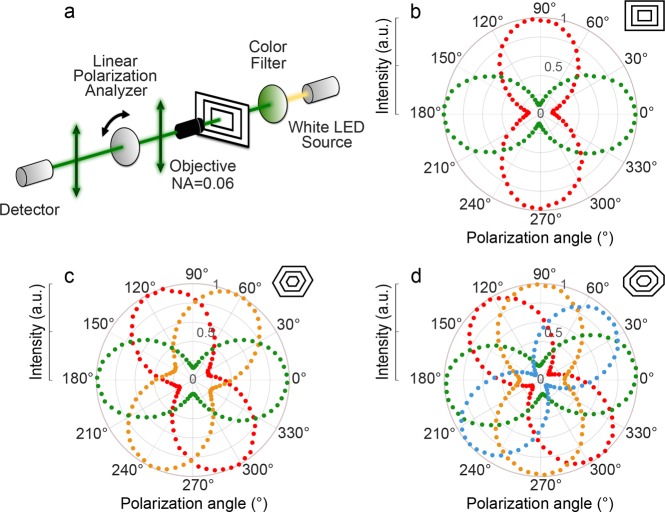
Figure 4.
Polarization-resolved spectroscopy. (a) Schematic of the detection scheme. A color filter is used to generate quasi-monochromatic light from a white-light source. Transmittance is collected using a numerical aperture of 0.06 and analyzed with a rotating linear polarizer. (b–d) Normalized transmitted intensity is measured as a function of polarization angle for different excitation wavelengths (red markers for λ = 650 ± 5 nm, orange for λ = 600 ± 5 nm, green for λ = 550 ± 5 nm, and blue for λ = 500 ± 5 nm) sent through a (b) rectangular, (c) hexagonal, and (d) octagonal multiresonant antenna.