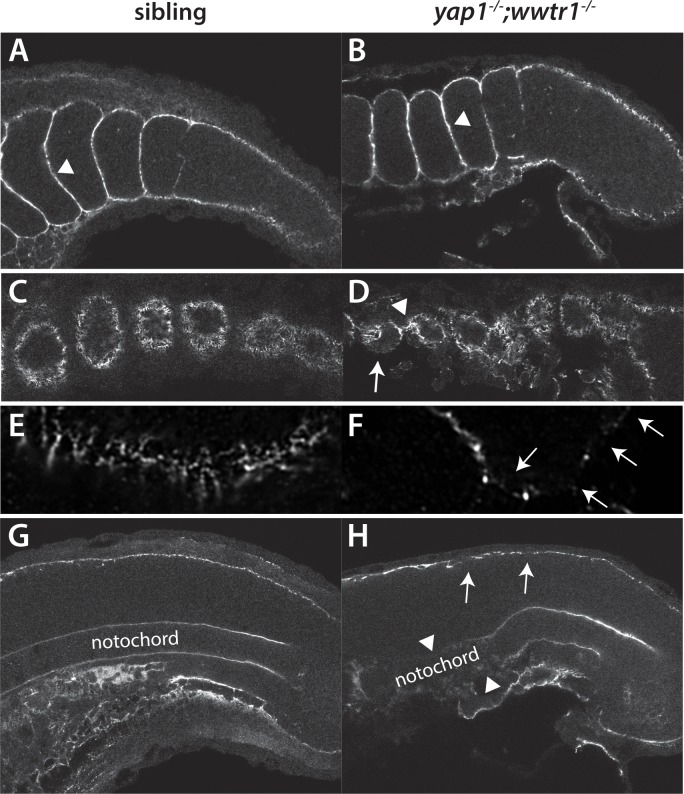
Figure 9. Fibronectin deposition is altered in yap1;wwtr1 double mutants.
(A,B) Intersomitic Fn deposition (arrowheads) appears unaffected in sibling and mutant embryos. Lateral confocal section. (C,D) At the lateral edges of the somites, Fn is present in rosettes where the somites contact the presumptive epidermis in sibling embryos (C), whereas in yap1;wwtr1 double mutants there are gaps (arrow) and regions of enhanced Fn accumulation (arrowhead, (D). (E, F) Higher magnification views of the ventral region of a single somite near its lateral edge from sibling (E) and yap1;wwtr1 double mutant (F) embryos showing altered Fn accumulation in the mutants. Arrows point to gaps in Fn deposition. (G,H) At the midline, Fn is discontinuous underneath the presumptive epidermis in yap1;wwtr1 double mutants (arrows, (H) compared to siblings (G)). The posterior notochord Fn staining appears mostly unaffected in yap1;wwtr1 double mutants, whereas in more anterior regions the Fn staining is absent (arrowheads), unlike in the siblings. All embryos are at 18-somites with anterior to the left.
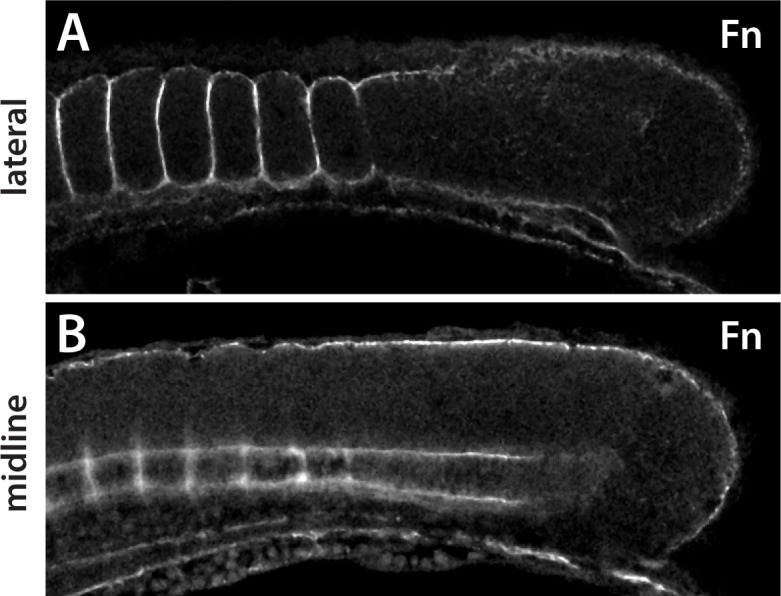
Figure 9—figure supplement 1. Expression of Fn in medaka embryos.