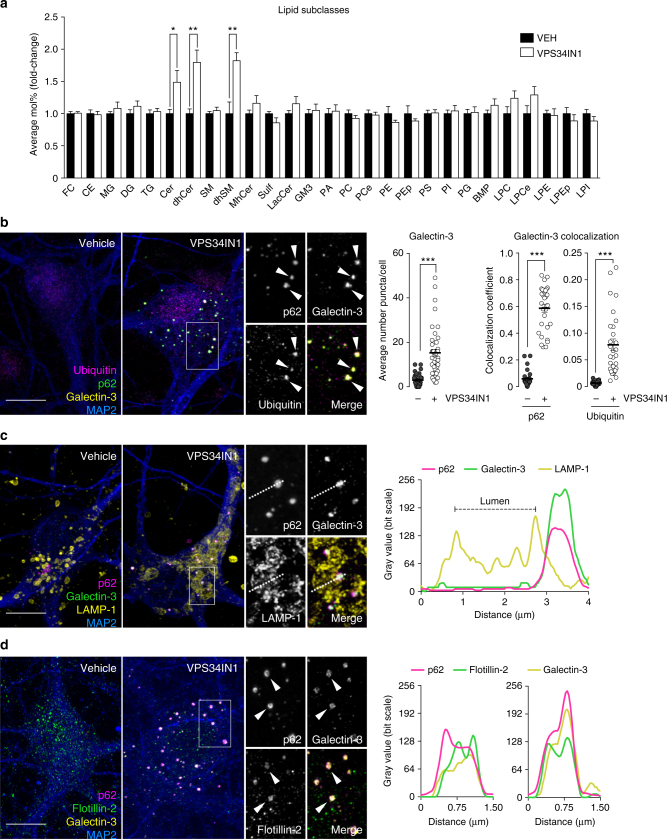
Fig. 3.
Vps34 inhibition causes cellular accumulation of sphingolipids and induces endolysosomal membrane damage. a LC–MS analysis of lipids extracted from primary cortical neurons treated with vehicle or VPS34IN1 at 3 µM for 24 h. For lipid nomenclature, see Methods section. Values are expressed as average Mol% of total lipid measured, normalized to vehicle (mean ± SEM, N = 8, from two independent experiments). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 in two-tailed Student’s t test. b–d Representative confocal images of cultured cortical neurons treated as in a. b Airyscan insets highlight triple colocalization between galectin-3, ubiquitin, and p62. Bar graphs indicate average number of galectin-3 puncta per cell (mean ± SEM, N = 40 cells, from three independent experiments), fraction of galectin-3 colocalizing with p62, and ubiquitin colocalizing with galectin-3 (mean ± SEM, N = 30 cells, from three independent experiments). c Airyscan insets highlight p62 and galectin-3 colocalization in close proximity to LAMP-1-positive membranes. Right panel, linescan intensity profile for adjacent p62/galectin-3 and LAMP-1 structures. d Airyscan insets and linescan intensity profile highlight triple colocalization between galectin-3, p62, and flotillin-2. Scale bar, 10 µm